단순헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순포진), Herpes simplex virus infections
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병의 원인
-
헤르페스바이러스(Herpes simplex virus/HSV)를 허피스바이러스, 단순 포진 바이러스, 헐피스 바이러스, 또는 (수)포진 바이러스라고도 한다.
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염에 의해 생긴 급성 바이러스 감염병을 단순 포진 바이러스 감염병, 단순 포진, 또는 허피스바이러스 감염이라고도 한다.
단순 헤르페스바이러스의 종류
-
헤르페스바이러스를
-
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)와
-
2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2)로 나눈다.
-
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병의 종류
1. 1형 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병
-
1형 헤르페스바이러스는 배꼽의 위 신체 부위에 주로 감염병을 일으킨다. 그러나 요즘은 배꼽 아래 신체 부위 신체에도 많이 감염된다.
-
헤르페스구내염(헐퍼스성 치은구강염/헤르페스바이러스 구내염)이나 입술 주위에 생기는 단순 포진 바이러스 감염병(열성 포진/Fever blister/콜드 소어/Cold sore) 등은 주로 1형 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴다.
-
1형 헤르페스바이러스 피부 발진이나 헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염(치은구강염) 등이 생겼을 때 환부를 육안으로 검진하고 어떤 형의 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴 치은구내염인지 또는 어떤 형의 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴 피부 발진인지 확실히 감별 진단할 수 없다.
-
때로는 1형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이나 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 상체나 하체를 가리지 않고 신체 어느 부위에도 생길 수 있다.
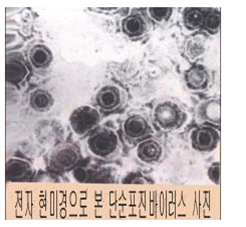
사진 4-1.헤르페스바이러스 사진.
출처–미 CDC 49
2. 2형 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(HSV-2 Infection)
-
2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병은 주로 배꼽의 아래에 있는 신체 부위에 생긴다. 그러나 요즘은 배꼽 위 신체 부위에도 많이 감염된다. 특히 성인들의 외부 생식기 부분에 감염되어 거기에 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
즉 2형 헤르페스바이러스는 주로 성인 남녀의 외부생식기 부위에 헤르페스바이러스 발진을 일으킨다.
-
신생아 헤르페스바이러스 감염병의 주 원인도 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염이다. 신생아 헤르페스 바이러스 감염병이 헤르페스바이러스 1형 감염으로도 생길 수 있다.
-
2형 헤르페스바이러스 질염이나 외음부염을 가지고 있는 임산부로부터 태어난 신생아에게 2형 헤르페스바이러스 뇌염이나 2형 헤르페스바이러스 피부염이 심하게 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 사망할 수 있다(바이러스 뇌염 참조).
-
2형 헤르페스바이러스 외음부염이 있는 사춘기 아이들이나 성인 남녀들이 오랄섹스를 할 때 2형 헤르페스바이러스가 입안에 감염되어 2형 헤르페스바이러스 구강염이 생길 수 있고 인두염도 생길 수 있다.
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병의 증상 징후
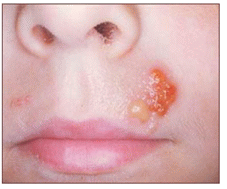
사진 4-2. 헤르페스바이러스 단순 포진 피부염
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
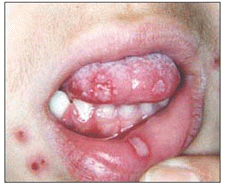
사진 4-3. 헤르페스바이러스 치은구강염(헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염)과 단순 포진
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 감염병)이 신체의 어느 부위에 생겨 있는지, 그 중증도, 병일, 나이 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
신생아들에게 생긴 단순 포진 바이러스 감염병과 신생아기 이후 영유아기나 학령기, 사춘기의 아이들에게 생긴 단순 포진 바이러스 감염병의 증상 징후에 차이가 많이 있다.
-
대부분의 경우, 신생아기 이후 소아청소년들이 헤르페스바이러스(단순 포진 바이러스)에 감염되면 불현성 감염이 생길 수 있다.
-
더러는 첫 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 입술, 또는 신체 다른 피부에 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 피부 발진)을 일으킬 수 있다. 이런 감염을 원발성 단순 포진이라고 한다.
-
단순 포진 바이러스 피부 발진을 일으킬 수도 있고,
-
때로는 헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염 및, 또는 헤르페스바이러스 인두염을 일으킨다.
-
1 형 헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염(헤르페스바이러스 치은 구강염 참조)의 증상 징후가 나타나기 시작한 후 7~10일 경 헤르페스바이러스가 입술과 입술 가장자리에 감염되어 입술 헤르페스(Herpes labialis) 감염병이 생길 수 있고 거기에 물집이 생기고 딱지가 지고 근질근질 가려우면서 아플 수 있다.
-
코의 바로 밑 부위와 윗입술 사이 또는 아랫입술 부위 피부에 1형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 발진) 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
그 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 생긴 피부가 따끔거리고 가렵고 좀 아플 수 있으나 대개 열은 나지 않는다.
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생겼던 원발성 헤르페스바이러스 피부염이 다 나은 후 몇 달 내지 몇 년 후에
-
피곤하거나,
-
월경 하거나,
-
스트레스를 많이 받고 긴장하거나,
-
뜨거운 햇볕에 오랫동안 노출되거나,
-
고열이 나는 어떤 감염병을 앓을 때나,
-
또는 그 외 다른 이유로 스트레스를 받을 때
-
-
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 피부 발진)이 과거에 났던 똑같은 부위 피부나, 다른 부위 피부에 또다시 날 수 있다.
-
이런 헤르페스바이러스 감염병을 재발성 헤르페스 병변, 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 또는 재발성 헤르페스라고 한다.
-
이렇게 생긴 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(포진)을 단순 포진(단순 헤르페스 Herpes simplex)이라고도 하고 입술 주위에 생기는 헤르페스바이러스 피부염을 열성 포진(Fever blister), 또는 콜드 소어(Cold sore)라고도 한다.
-
재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 피곤하거나, 월경 하거나, 많이 긴장되거나, 뜨거운 햇볕에 오랫동안 노출되거나, 고열이 나거나 그 외 문제로 유발되기 때문에 그런 유발 인자를 될 수 있는 한 피해 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염의 재발을 예방해야 한다.
-
신생아기 이후 생기는 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 피부 발진)의 잠복기는 약 3~10일이다.
-
외음부 헤르페스바이러스가 사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 감염되어 1차 HSV 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
헤르페스 바이러스가 여성이나 남성의 외음부나 회음부 또는 양 두 부위에 동시 감염되어 피부에 포진이 생기고 그 포진에 괴양이 생길 수 있다.
-
미국에서는 HSV-2와 HSV-1가 거의 같은 비율로 외음부 헤르페스바이러스 감염병을 일으킨다고 한다. 외음부 헤르페스바이러스 감염병은 대개 무 증상이다.
-
습진(아토피성 피부염)이 있는 아이들의 피부에 헤르페스 바이러스가 감염되면 그 증상 징후가 훨씬 심하다.
-
면역체계 기능 이상이 있는 사람에게 헤르페스 바이러스 감염병이 생기면 그 증상 징후가 훨씬 심하다.
-
헤르페스 바이러스에 맨 처음 감염된 후 잠재성 감염병 상태로 일생동안 계속 될 수 있다. 잠재성 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 있을 때 대개 무 증상이다. 잠재성 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 활동성 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 상태로 외음기, 음낭, 여성의 외음, 자궁경부, 엉덩이, 항문주위, 대퇴부에 생겨 습포가 날 수 있다.
-
눈에 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 1차적 또는 재발로 생겨 결막염, 각막염이 생길 수 있다.
-
손가락 끝 부위에 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 생길 수 있다.
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 뇌염, 뇌막염 등이 생길 수 있고
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염병으로 벨스 마비, 3차 뇌신경 신경통, 재발성 뇌막염, 감염 후 뇌척수염 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
그 외 신체 여러 부위에 감염되어 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 생긴다.
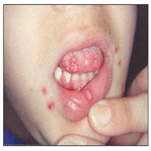
사진 4-4. 헤르페스바이러스
치은구강염(헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염)과 단순포진
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
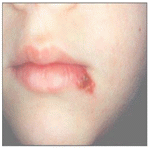
사진 4-5. 헤르페스바이러스 치은구강염(헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염)과 단순포진 Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
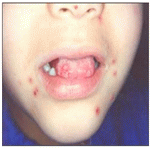
사진 4-6. 단순 포진과 헤르페스바이러스 치은 구내염(치은 구강염)
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
-
환부에 있는 피고름이나 분비물로 바이러스 배양을 하거나, 또는 환부 생체조직 검사를 하거나 현미경 짱크 검사(Tzanck Test)로 진단한다.
-
헤르판지나 인두염(헤르판지나/Herpangina), 아프타스 궤양, 수족구병, 접촉성 피부염 등과 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, IgG 항체 검사로 진단 할 수도 있다.
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병의 치료
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴 피부 점막 감염병은 의사의 처방에 따라 경구용 Acyclovir, Famciclovir, 또는 Valacylovir 등으로 치료할 수 있다. 국소 도포용 Docosanol 10% 크림, 또는 국소 도포용 Penciclovir 1% 크림 등으로 국소도포치료할 수 있으나 이런 약으로 통상적 치료를 하지 않는다. 에이사이클로비아(Acyclovir) 연고로 치료하면 잘 치료되는 경험을 저자는 가지고 있다. 국소 도포용 Docosanol 10% 크림, 또는 국소 도포용 Penciclovir 1% 크림 등으로 국소도포 치료할 수 있다. 그러나 이런 약으로 통상적 치료를 하지 않는다.
-
헤르페스바이러스가 외음부에 감염될 때는 경구용 에이사이클로비아로 10일 간 치료한다. Valacyclovior과 Famciclovior 치료는 에이사이클로비아 치료보다 더 효과적은 아니다. 헤르페스바이러스 외음부 감염에다 심한 합병증이 있을 때는 에이사이클로비아혈관주사로 치료한다. 재발성이 있는 성인 외음부 감염병을 경구용 에이사이클로비아로 치료하기도 한다. 경구용 에이사이클로비아로 재발성 성인 헤르페스바이러스 외음부 염을 예방하기도 한다.
-
1형 헤르페스바이러스 감염성 피부염을 에이사이클로비아나 펜시클로버 연고로 조기 치료하면 치료효과가 좋다.
-
단순 포진 바이러스 감염으로 인한 피부염이 생기면 충분한 휴식과 영양분을 섭취하며 타이레놀이나 코데인 등으로 진통시킬 수 있다. 대개 7~10일 이내에 잘 낫는다.
-
1형 단순 포진 바이러스 피부염이 다 나은 후에 피부에 흉터가 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 치료용 항 바이러스제
1. Acyclovir,
2. Valacyclovir,
3. Famciclovir,
4. Penciclovir,
5. Vidarabine
등이 있다.
-
Valtrex(Valacylovir hydrchloride)로 2~18세 소아들의 수두를 치료할 수 있고 12세와 그 상 먹은 사춘기 아이들의 입술 헤르페스바이러스 감염(콜드소아/Cold sore)을 치료할 수 있다. 신생아 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 (신생아 단순 포진 바이러스 감염병)
-
잠복기는 약 4주이고 출생 후 어느 때나 발병될 수 있다.
-
출생 전 태반이나 산도에서 감염될 수 있고
-
드물게는 분만 중 모체 외부생식기에 있는 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 병소에서
-
또는 질강 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 병소에서 감염될 수 있다.
단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 신생아에게 발생되면
-
헤르페스바이러스-1(HSV-1)이나 헤르페스바이러스-2(HSV-2)가 신생아에게 감염될 수 있다. 일단 감염되면 그 바이러스가 전신으로 퍼져 다음과 같은 신체의 여러 기관에 감염될 수 있다.
-
중추 신경계뿐만 아니라 간, 폐 등 전신 모든 기관 신생아 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 생길 수 있다. 그래서 박테리아 패혈증을 앓는 것과 유사하게 몹시 심하게 앓을 수 있다.
-
헤르페스바이러스는 중추 신경계에 한정되어 감염되어 그에 따른 증상 징후가 나타날 수도 있고, 어떤 병을 앓는지 확실히 모를 정도로 특이한 증상 징후가 나타나지 않을 수 있다. 그래서 이병의 초기에 진단을 확실히 나릴 수 없는 경우도 있다.
-
피부, 눈, 입 등 신체의 어떤 부위에 한정 된 신생아 헤르페스바이러스 감염병이 생길 수 있고
-
열이 나고 보채고 예민한 증상 징후가 신생아에게 생길 수 있고 뇌척수 액 검사의 결과가 비정상적이고, 특히 신생아가 전신 경련을 하면 신생아 헤르페스바이러스 감염병을 의심해야 한다.
-
신생아 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 신생아 중추 신경계에 있으면 0.3%~1.0%에서 열이 나고 척수 액 검사가 비정상적이다(Archies of pediatrics and adolescent medicine, July 2008, p.665).
-
피부, 눈, 입 등에 한정된 헤르페스바이러스 감염을 앓을 수도 있다.
-
헤르페스바이러스 감염이 피부에 생기면 습포가 그룹으로 나고 어떤 수포에는 딱지가 지고, 어떤 습포에 궤양이 생기기도 한다. 그리고 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 뇌염, 간염, 폐렴 등이 생길 수 있다. 잠복기는 생 후 6주 정도이다.
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰 소견 등을 종합하고 짱크 검사, 형광 항체검사, 구강, 비이두강, 결막, 한문, 척수액 등 피검물로 PCR 분석 검사, ALT 검사, ELISA 검사, 세포 배양 검사, EIA 검사, 바이러스 배양검사 등으로 진단한다.
-
헤르페스바이러스 신생아 뇌염은 병원에서
① 에이사이클로비아(Acyclovir) 혈관주사로 적어도 21동안 치료한다.
그 후 6개월 동안 경구용 에이사이클로비아로
치료한다.
② Famciclovir(Famvir)
③ 또는 Valacyclovir(Valtrex) 혈관주사로 치료한다.
④ 때로는 비다라빈(Vidarabine) 혈관주사 치료도 한다.
-
그 중 에이사이클로비아 혈관주사 치료를 가장 많이 쓴다.
-
눈에 감염된 헤르페스바이러스 신생아 감염은 국소 안약(trifluridine, iododeoxyuridine, 또는 ganciclovior) + 혈관 항 바이러스제로 치료한다.
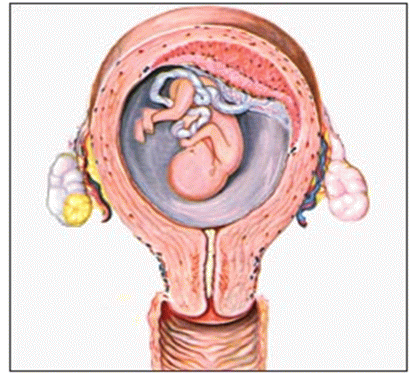
그림 4-7. 임신 중 자궁 내 태아가 모체에서 2형 헤르페스바이러스에 감염되어 선천성 신생아 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병에 걸릴 수 있다.
그리고 임신부의 질 산도에서 2형 헤르페스바이러스에 감염되어 신생아가 2형 헤르페스바이러스 감염병에 걸릴 수 있다.
태아 헤르페스바이러스 감염병은 TORCH(TORCH 참조)에 속한다.
출처: 소아 가정의학백과와 Used with permission from “Illustrations from Pregnancy in Anatomical Illustrations appear courtesy of the copyright owner Carnation Company, Los Angeles, CA 1962”
표로 보는 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 감염병/허피스바이러스 감염병) Herpes simplex virus infections
|
|
|
|||
|
헤르페스바이러스 감염병의 종류 |
||||
|
단순 헤르페스구내염(헐퍼스성 치은구강염/단순 헤르페스바이러스 구내염) |
||||
|
원인 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)나 2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2) |
|||
|
증상 |
1 형 헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염(헤르페스바이러스 치은 구강염 참조)의 증상 징후가 나타나기 시작한 후 7~10일 경 헤르페스바이러스가 입술과 입술 가장자리에 감염되어 입술 헤르페스(Herpes labialis) 감염병이 생길 수 있고 거기에 물집이 생기고 딱지가 지고 근질근질 가려우면서 아플 수 있다. |
|||
|
진단 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스 피부 발진이나 헤르페스바이러스 치은구내염(치은구강염) 등이 생겼을 때 환부를 육안으로 검진하고 어떤 형의 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴 치은구내염인지 또는 어떤 형의 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴 피부 발진인지 확실히 감별 진단할 수 없다 |
|||
|
치료 |
무증상 헤르페스 감염은 관찰 치료를 하고 한다. 치은 구내염, 초기 생식기 해르페스, 습진 헤르페스, 면역 결손 헤르페스, 입술 헤르페스 재발성 생식기 헤르페스, 헤르페스 결막각막염, 헤르페스 생인손, 헤르페스 뇌염, 헤르페스 뇌막염, 헤르페스 벨스마비, 비전형적인 통증 증후군, 3차 신경 신경통, 감염 후 뇌척수염은 중증도, 감염된 신체 부위에 따라 또는 면역 적격 또는 손상의 유무에 따라, 나이에 따라 경구 Acyclovir나, Valacyclovir, 또는 Famciclovir 등 항 바이러스체로 치료 한다 |
|||
|
■ 단순 포진 바이러스 감염병(열성 포진/Fever blister/콜드 소어/Cold sore) 등은 주로 1형 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염으로 생긴 |
||||
|
원인 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)나 2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2) |
|||
|
증상 징후 |
헤르페스바이러스 감염병(단순 포진 바이러스 감염병)이 신체의 어느 부위에 생겨 있는지, 그 중증도, 병일, 나이 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다. |
|||
|
진단 |
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다. 환부에 있는 피고름이나 분비물로 바이러스 배양을 하거나, 또는 환부 생체조직 검사를 하거나 현미경 짱크 검사(Tzanck Test)로 진단한다. 헤르판지나 인두염(헤르판지나/Herpangina), 아프타스 궤양, 수족구병, 접촉성 피부염 등과 감별 진단해야 한다. PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, IgG 항체 검사로 진단 할 수도 있다. |
|||
|
치료 |
무증상 헤르페스 감염은 관찰 치료를 하고 한다. 치은 구내염, 초기 생식기 해르페스, 습진 헤르페스, 면역 결손 헤르페스, 입술 헤르페스 재발성 생식기 헤르페스, 헤르페스 결막각막염, 헤르페스 생인손, 헤르페스 뇌염, 헤르페스 뇌막염, 헤르페스 벨스마비, 비전형적인 통증 증후군, 3차 신경 신경통, 감염 후 뇌척수염은 중증도, 감염된 신체 부위에 따라 또는 면역 적격 또는 손상의 유무에 따라, 나이에 따라 경구 Acyclovir나, Valacyclovir, 또는 Famciclovir 등 항 바이러스체로 치료 한다 |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
재발성 단순 헤르페스 병변(재발성 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 또는 재발성 헤르페스) |
|||
|
원인 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)나 2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2)이다. 입술 주위에 생기는 헤르페스바이러스 피부염(열성 포진(Fever blister), 또는 콜드 소어(Cold sore)을 앓은 후 피곤하거나, 월경 하거나, 많이 긴장되거나, 뜨거운 햇볕에 오랫동안 노출되거나, 고열이 나거나 그 외 여러 가지 문제로 스트레스를 많이 받으면 열성 포진이 유발되기 쉽다. 재발성 생식기 헤르페스바이러스 감염병은 헤르페스 바이러스 재활정화로 생길 수 있고 다시 감염돼서 생길 수 있다. |
|||
|
증상 징후 |
초기 감염의 증상 징후와 거의 같다. |
|||
|
진단 |
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다. 환부에 있는 피고름이나 분비물로 바이러스 배양을 하거나, 또는 환부 생체조직 검사를 하거나 현미경 짱크 검사(Tzanck Test)로 진단한다. 헤르판지나 인두염(헤르판지나/Herpangina), 아프타스 궤양, 수족구병, 접촉성 피부염 등과 감별 진단해야 한다. PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, IgG 항체 검사로도 진단할 수 있다. |
|||
|
치료, 예방 |
경구 Acyclovir나, Valacyclovir, 또는 Famciclovir으로 예방치료한다. 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 피곤하거나, 월경하거나, 많이 긴장되거나, 뜨거운 햇볕에 오랫동안 노출되거나, 고열이 나거나 그 외 문제로 유발되기 때문에 그런 유발 인자를 될 수 있는 한 피해 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염의 재발을 예방해야 한다 |
|||
|
|
||||
|
헤르페스 바이러스 감염병의 종류 |
생식기 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 |
|
|
원인 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)나 2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2)이다. 재발성 생식기 헤르페스바이러스 감염병은 헤르페스 바이러스 재활정화로 생길 수 있고 다시 감염돼서 생길 수 있다. |
|
|
증상 징후 |
습포 궤양 등이 남성이나 여성의 외음기나 회음부 또는 두 부위에 생길 수 있다. 대부분의 초기 생식기 헤르페스 감염은 무증상이다. |
|
|
진단 |
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다. 환부에 있는 피고름이나 분비물로 바이러스 배양을 하거나, 또는 환부 생체조직 검사를 하거나 현미경 짱크 검사(Tzanck Test)로 진단한다. 헤르판지나 인두염(헤르판지나/Herpangina), 아프타스 궤양, 수족구병, 접촉성 피부염 등과 감별 진단해야 한다. PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, IgG 항체 검사로도 진단 할 수 있다. |
|
|
치료, 예방 |
경구 Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, 또는 Famciclovir으로 예방치료한다. 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 피곤하거나, 월경하거나, 많이 긴장되거나, 뜨거운 햇볕에 오랫동안 노출되거나, 고열이 나거나 그 외 문제로 유발되기 때문에 그런 유발 인자를 될 수 있는 한 피해 재발성 헤르페스바이러스 감염의 재발을 예방해야 한다. Pretelivir로 치료 한 결과가 좋다고 한다 The NEJM 1/16/2014. |
|
|
헤르페스 바이러스 감염병의 종류 |
신생아 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 |
|
|
원인 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)나 2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2) 감염으로 이 병이 생길 수 있다. 헤르페스바이러스에 감염된 분만부 생식기에서 출산 시 감염되기도 하고 때로는 외 분만부의 생식기에 있는 헤르페스바이러스가 양막 파손의 유무에 관계없이 상행 전파되어 태어나는 아기에게 헤르페스바이러스를 감염시킬 수 있다. 또 출생 후 부모나 아기 돌봐주는 사람들의 입이나 손에 감염된 헤르페스바이러스 감염병으로부터 감염될 수도 있다. 드물게는 자궁 내 태아가 감염될 수도 있다. |
|
|
증상 징후 |
여러 기관에 감염되어 파종 감염병이 생길 수 있다. 간과 폐, 피부, 입, 눈, 중추신경에 감염된다. 피부, 국소 헤르페스바이러스 감염이 없이 중추신경 감염만 생길 수도 있다. 때로는 피부, 눈, 또는 입에도 감염될 수 있다. 눈이나 피부 또는 입에 생긴 국소 감염만 발생할 수도 있다. 신생아에서 열이 나고 습포가 생기고 뇌척수액 검사 이상이 있고 경련이 있을 때는 중추신경 헤르페스 감염이 있다고 추정 진단할 수 있다. 사망률이 상당히 높고 영유아 때 재발성 피부염도 생길 수 있다. 출생 후부터 6주 이내 어느 때든지 발병할 수 있다. |
|
|
진단 |
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다. 환부에 있는 피고름이나 분비물로 바이러스 배양을 하거나, 또는 환부 생체조직 검사를 하거나 현미경 짱크 검사(Tzanck Test)로 진단한다. 헤르판지나 인두염(헤르판지나/Herpangina), 아프타스 궤양, 수족구병, 접촉성 피부염 등과 감별 진단해야 한다. PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, IgG 항체 검사로도 진단 할 수 있다. |
|
|
치료 예방 |
혈관 Acyclovir로 치료한다. 신생아 눈 헤르페스바이러스 감염병은 혈관 Acyclovir + 안약(1% trifluridine, 0.1% iododeoxyuridine, 또는 0.15%ganciclovir)으로 치료한다. |
|
|
헤르페스 바이러스 감염병의 종류 |
신생아기 이후 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들에게 생기는 단순 헤르페스바이러스 감염병 |
|
|
원인 |
1형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-1)나 2형 헤르페스바이러스(HSV-2) 감염으로 다음과 같은 헤르페스 바이러스 감염병에 생길 수 있다.있다. |
|
|
증상 징후 |
무증상 헤르페스–신생아기 이후 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들에게 생기는 초기 헤르페스바이러스 감염의 대부분은 무증상이다. 신생아 헤르페스–헤르페스 바이러스 감염이 있는 무든 신생아는 혈관 에이사이클러비아(Acylovir)로 치료한다. 헤르페스 바이러스성 뇌염, 피부염, 눈 감염, 점막 감염이 신생아에게 생기면 Acylovir로 치료한다. 뇌 MRI, 울트라사운드 영상, 뇌척수액 검사로 진단, 추적 치료를 한다. 치은 구내염–HSV-1감염으로 생기며 신생아기 이후 생기는 헤르페스 바이러스 감염병 중 흔한 감염병이다. 열, 과민, 턱밑 림프절 비대, 치주 및 구강점막 궤양 등이 생긴다. 생식기 해르페스–사춘기 아이들이나 성인들의 생식기 헤르페스 감염병이 생기면 여성이나 남성의 생식기에 습포와 궤양이 생길 수 있다. 대부분의 경우, 무증상일 수도 있다. HSV-1 헤르페스 바이러스 감염이나 HSV-2 헤르페스 바이러스 감염으로 생긴다. 습진 헤르페스– 아토피성 피부염이 있는 아이들에게 헤르페스 바이러스가 감염되면 습진 헤르페스가 생기고 그로인해 출혈 딱지가 생기고 습포 및 움푹 파진 습포 등이 생긴다. 면역 결손 헤르페스–심한 국소 감염증도 생기고 파종성 전신 감염 병이 생길 수 있다. 입술 헤르페스–1차 감염된 후 일생동안 잠재 감염으로 남아있을 수 있다. 1차 감염이 나은 후 여러 가지 이유로 인해 HSV-1 헤르페스 재발 입술 헤르페스감염이 생길 수 있다. 이때 입 주위, 홍순, 입술가장자리 등에 한 개나 여러 개의 습포가 생길 수 있다. 이런 습포를 영어로 Cold sores 또는 fever blisters(열 습포)라고 한다. 재발성 생식기 헤르페스–1차 생식기 헤르페스기 생겼다가 나은 후 재발되면 음경, 음낭, 외음, 자궁경두, 엉덩이, 음부, 회음부, 사타구니 등에 습포가 하나 둘이나 여러 개가 군집으로 날 수 있다. 면역 결손이 있는 사람에게 HSV-2 재발성 생식기 헤르페스 감염이 생기면 증상이 훨씬 심하고 자주 재발하고 한번 생기면 그 증상이 오래간다. 그리고 더 화끈거리고 더 가렵다. 헤르페스 결막각막염–1차적으로도 생길 수 있고 재발할 수도 있다. 헤르페스 생인손–헤르페스 습포가 한 개–여러 개가 손가락의 끝 마디에 생실 수 있다. 헤르페스 뇌염–신생아기 이후 소아들이나 사춘기 아이들의 뇌 HSV-1 헤르페스 바이러스 감염으로 뇌염이 생길 수 있다. 이때 생기는 뇌염은 1차적으로나 또는 재발성으로 생길 수 있다. 열, 의식의 변화, 성격 변화, 경련, 신경장애, 혼수 등이 생길 수 있다. 그리고 사망할 수 있다. 헤르페스 뇌막염이 주로 HSV-2 헤르페스 바이러스 감염으로 생긴다. 헤르페스 벨스마비, 비전형적인 통증 증후군, 3차 신경 신경통, 감염 후 뇌척수염 등도 헤르페스 바이러스 감염으로 생길 수 있다. |
|
|
진단 |
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 진단할 수 있다. 환부에 있는 피고름이나 분비물로 바이러스 배양을 하거나, 또는 환부 생체조직 검사를 하거나 현미경 짱크 검사(Tzanck Test)로 진단한다. PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, IgG 항체 검사로도 진단 할 수 있다. 헤르판지나 인두염(헤르판지나/Herpangina), 아프타스 궤양, 수족구병, 접촉성 피부염 등과 감별 진단해야 한다. |
|
|
치료 예방 |
무증상 헤르페스 감염병은 관찰 치료를 하고 한다. 치은 구내염, 초기 생식기 해르페스, 습진 헤르페스, 면역 결손 헤르페스, 입술 헤르페스 재발성 생식기 헤르페스, 헤르페스 결막각막염, 헤르페스 생인손, 헤르페스 뇌염, 헤르페스 뇌막염, 헤르페스 벨스마비, 비전형적인 통증 증후군, 3차 신경 신경통, 감염 후 뇌척수염은 중증도, 감염된 신체 부위에 따라 또는 면역 적격 또는 손상의 유무에 따라, 나이에 따라 경구 Acyclovir나, Valacyclovir, 또는 Famciclovir 등 항 바이러스체로 치료 한다. |
|
Herpes simplex virus infections
Causes of herpes simplex virus infection
• Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is also called herpes virus, herpes simplex virus, herpes virus, or herpes (male) virus.
• Acute viral infections caused by herpes virus infection are also called herpes simplex virus infection, herpes simplex virus infection, or herpes simplex virus infection.
Types of herpes simplex virus
• Herpesvirus o Herpesvirus type 1 (HSV-1) and o It is classified as herpesvirus type 2 (HSV-2). Types of herpes simplex virus infection
1. Herpes simplex virus type 1 infectious disease
• Herpesvirus type 1 mainly infects the body area above the navel. However, these days, many parts of the body below the navel are also infected.
• Herpes stomatitis (herpes gingivitis/herpesvirus stomatitis) or herpes simplex virus infection around the lips (herpes febrile/fever blister/cold sore) are mainly caused by herpesvirus type 1 infection.
• When a herpesvirus type 1 skin rash or herpesvirus gingivostomatitis (gingivostomatitis) occurs, visually examine the affected area and make sure it is a skin rash caused by a type of herpes virus infection or a type of herpesvirus infection. cannot be differentially diagnosed.
• Occasionally, herpesvirus type 1 or type 2 herpes virus infection can occur anywhere on the body, upper or lower body.

Picture 4-1. Herpes virus picture. Source – US CDC 49
2. Herpes simplex virus type 2 infectious disease
• Herpesvirus type 2 infection mainly occurs in the body area below the navel. However, these days, many parts of the body above the navel are also infected. In particular, it can infect the external genital area of adults and cause herpes virus type 2 infection there.
• In other words, herpesvirus type 2 mainly causes herpes virus outbreaks in the external genital area of male and female adults.
• The main cause of neonatal herpes virus infection is herpes virus type 2 infection. Neonatal herpes virus infection can also be caused by herpesvirus type 1 infection.
• Newborns born to pregnant women with herpesvirus vaginitis or vulvitis can develop severe herpesvirus encephalitis or herpesvirus dermatitis, which can result in death (see Viral Encephalitis).
• Adolescent children or adults with herpes vulvitis type 2 can get herpes type 2 virus in their mouths and develop pharyngitis and herpes virus stomatitis when they have oral sex.
Symptoms of herpes simplex virus infection

Photo 4-2. herpesvirus herpes simplex dermatitis Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-3. Herpesvirus gingivostomatitis (herpesvirus gingivostomatitis) and herpes simplex Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Symptoms of herpes virus infection (herpes simplex virus) vary depending on the body part, the severity, the disease day, and age.
• There are many differences in the symptoms and signs of herpes simplex virus infection in newborns and herpes simplex virus infection in infants, school-age children, and adolescents after the neonatal period.
• In most cases, subclinical infections can occur when children and adolescents become infected with the herpes virus (herpes simplex virus) after the neonatal period. • In some cases, the first herpes virus infection can cause a herpes virus infection (herpes simplex virus skin rash) on the lips or other skin on the body. This infection is called primary herpes simplex.
• Herpes simplex virus may cause a skin rash;
• Occasionally causes herpesvirus gingivostomatitis and/or herpesvirus pharyngitis.
• About 7 to 10 days after the onset of symptoms of herpesvirus type 1 gingival stomatitis (see Herpesvirus gingival stomatitis), the herpes virus can infect the lips and the edges of the lips, causing Herpes labialis infection and blistering there. It can become painful, scab and itchy, itchy and painful.
• Herpes simplex virus (herpes simplex virus rash) may develop on the skin just under the nose and between the upper lip or on the lower lip area.
• The skin affected by the herpes virus infection may sting, itchy, and a little sore, but usually there is no fever.
• Months to years after primary herpesvirus dermatitis caused by herpesvirus infection has cleared up
o Tired or
o menstruation,
o If you are very stressed or nervous,
o Prolonged exposure to hot sun,
o When suffering from any infectious disease with high fever,
o When you are stressed or for any other reason
• Herpes simplex virus infection (herpes simplex virus skin rash) can reappear on the same skin area as it occurred in the past, or on a different area of the skin.
• These herpesvirus infections are called recurrent herpes lesions, recurrent herpesvirus infections, or recurrent herpes.
• This recurrent herpes virus infection (herpes) is also called herpes simplex, and herpesvirus dermatitis around the lips is also called fever blister or cold sore.
• Damage as much as possible because the recurrent herpes virus infection is caused by fatigue, menstruation, being very nervous, prolonged exposure to the sun, high fever, or other problems. Recurrence of recurrent herpesvirus infection. should be prevented
• The incubation period of herpesvirus infection (herpes simplex virus skin rash) that occurs after the neonatal period is about 3 to 10 days.
• Vulvar herpesvirus can infect adolescents and adults, resulting in primary HSV infections.
• The herpes virus can co-infect the vulva, perineum, or both areas of a woman or man, causing herpes to form on the skin and a lump in the herpes.
• In the United States, it is reported that HSV-2 and HSV-1 cause vulvar herpesvirus infections in approximately equal proportions. Vulvar herpesvirus infections are usually asymptomatic.
• When the herpes virus infects the skin of children with eczema (atopic dermatitis), the symptoms are much more severe.
• The symptoms of a herpes virus infection in a person with an impaired immune system are much more severe.
• After initial infection with the herpes virus, it can be a lifelong latent infectious disease. When a latent herpes virus infection is present, it is usually asymptomatic. Latent herpesvirus infection is a state of active herpesvirus infection, and blisters can form in the vulva, scrotum, vulva, cervix, buttocks, perianal area, and thigh.
• Conjunctivitis and keratitis may occur due to primary or recurrent eye herpes virus infection.
• A herpes virus infection may develop on the fingertips.
• Herpesvirus infection can cause encephalitis, meningitis, etc.
• Herpesvirus infection can cause Bell’s palsy, trigeminal neuralgia, recurrent meningitis, and post-infection encephalomyelitis.
• Infection of other parts of the body causes a herpes virus infection.

Photo 4-4. herpes virus Gingivostomatitis (herpesvirus gingivostomatitis) and herpes simplex Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-5. Herpes virus gingivostomatitis and herpes simplex Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-6. Herpes simplex and herpesvirus gingival stomatitis (gingival stomatitis) Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of herpes simplex virus infection
• This disease can be easily diagnosed by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
• Diagnosis is made by culturing the virus with blood pus or secretions in the affected area, or by performing a biopsy of the affected area or microscopic Tzanck Test.
• Differential diagnosis should be made from herpangina or pharyngitis (Herpangina), aphthous ulcer, hand, foot and mouth disease, and contact dermatitis.
• It can also be diagnosed by PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, and IgG antibody tests.
Treatment of herpes simplex virus infection
• Skin and mucosal infections caused by herpes virus infection can be treated with oral Acyclovir, Famciclovir, or Valacylobir according to a doctor’s prescription. Docosanol 10% cream for topical application or Penciclovir 1% cream for topical application can be applied topically, but these drugs are not usually used for treatment. The author has experience with treatment with Acyclovir ointment. Topical application of Docosanol 10% cream or Penciclovir 1% cream for topical application can be used for topical treatment. However, these drugs are not routinely treated.
• When the herpes virus infects the vulva, treat with oral acyclovir for 10 days. Treatment with valacyclovir and famciclovir is not more effective than treatment with acyclovir. When herpesvirus vulvar infection has severe complications, it is treated with acyclovir vascular injection. Oral acyclovir is also used to treat recurrent adult vulvar infections. Oral acyclovir is also used to prevent recurrent adult herpesvirus vulvitis.
• Early treatment of herpesvirus type 1 infectious dermatitis with acyclovir or penciclovir ointment is effective.
• If you develop dermatitis due to herpes simplex virus infection, you can take enough rest and nutrition, and use Tylenol or codeine for pain relief. It usually heals well within 7 to 10 days.
• After the herpes simplex virus dermatitis has cleared up, it is normal for the skin to leave no scars.
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infection
1. Acyclovir,
2. Valacyclovir,
3. Famciclovir,
4. Penciclovir,
5. Vidarabine
etc.
• Valtrex (Valacyclovir hydrchloride) can treat chickenpox in children 2 to 18 years old, and cold sores in adolescents 12 years old and older. Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus Infectious Disease (Newborn Herpes Simplex Virus Infectious Disease)
• The incubation period is about 4 weeks and the onset can occur at any time after birth. • Can be transmitted from the placenta or birth canal before birth
• Rarely, in lesions of type 2 herpesvirus infection in the maternal external genitalia during childbirth.
• Alternatively, infection can occur at the lesion of a vaginal type 2 herpesvirus infection.
When herpes simplex virus infection occurs in newborns
• Herpesvirus-1 (HSV-1) or herpesvirus-2 (HSV-2) can infect newborns. Once infected, the virus can spread throughout the body and infect multiple organs in the body, including:
• Not only the central nervous system, but also the liver and lungs can cause neonatal herpes virus infection in all organs. So it can be very severe, similar to having bacterial sepsis.
• The herpes virus is limited to the central nervous system and may cause symptoms and signs of infection, or may not show specific symptoms to the extent that it is unclear which disease you have. Therefore, in some cases, it is not possible to make a definitive diagnosis in the early stages of the disease.
• Newborn herpes virus infections that are limited to certain parts of the body, such as the skin, eyes, and mouth, can occur.
• Newborn herpesvirus infection should be suspected if fever, rash, and sensitive symptom signs may occur in newborns, cerebrospinal fluid test results are abnormal, and especially if the newborn has generalized convulsions.
• When neonatal herpesvirus infection is present in the neonatal central nervous system, fever occurs in 0.3% to 1.0% and spinal fluid examination is abnormal (Archies of pediatrics and adolescent medicine, July 2008, p.665).
• You may have a herpes virus infection that is limited to the skin, eyes, or mouth.
• When a herpes virus infection occurs on the skin, blisters form in groups, some blisters scab and some blisters form. And herpesvirus infection can cause encephalitis, hepatitis, pneumonia, etc. The incubation period is about 6 weeks after birth.
• Synthesize the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, and perform PCR analysis, ALT test, ELISA test, cell culture test, EIA test, Diagnosis by viral culture test. • Herpesvirus neonatal encephalitis
① Treat with acyclovir intravenous injection for at least 21 days. Thereafter, oral acyclovir was administered for 6 months. treat
② Famciclovir (Famvir)
③ or Valacyclovir (Valtrex) intravenous injection.
④ Sometimes, Vidarabine vascular injection is also treated.
• Among them, acyclovir vascular injection is the most used.
• Herpesvirus neonatal infection of the eye is treated with topical eye drops (trifluridine, iododeoxyuridine, or ganciclovir) plus vascular antiviral drugs.

Figure 4-7. During pregnancy, an intrauterine fetus may become infected with the herpes virus type 2 in the mother and contract the congenital neonatal type 2 herpes virus infection. In addition, a pregnant woman’s vaginal birth canal can become infected with the herpes virus type 2, and the newborn can contract the type 2 herpes virus infection. Fetal herpesvirus infectious diseases belong to TORCH (see TORCH). Source: Pediatric Family Medicine Encyclopedia Used with permission from “Illustrations from Pregnancy in Anatomical Illustrations appear courtesy of the copyright owner Carnation Company, Los Angeles, CA 1962”
Table Herpes simplex virus infections
|
|
Herpes simplex stomatitis (herpetic gingivostomatitis/herpes simplex virus stomatitis) |
|||
|
Types of herpes virus infection |
||||
|
Cause |
Herpes virus type 1 (HSV-1) or herpes type 2 virus (HSV-2) |
|||
|
symptoms, signs |
About 7 to 10 days after the symptoms of herpesvirus type 1 gingival stomatitis (see Herpesvirus gingival stomatitis) appear, the herpes virus can infect the lips and the edges of the lips, resulting in Herpes labialis infection, where blisters can form. It can become painful, itchy, itchy, and scabs. |
|||
|
diagnosis |
When a herpesvirus type 1 skin rash or herpesvirus gingivostomatitis (gingivostomatitis) occurs, visually examine the affected area and clearly distinguish whether it is gingival stomatitis caused by a herpesvirus infection or a skin rash caused by a herpesvirus infection. can’t diagnose |
|||
|
treatment |
Asymptomatic herpes infections are treated with observation. gingival stomatitis, early genital herpes, eczema herpes, immunodeficiency herpes, Herpes lip recurrent genital herpes, herpes conjunctival keratitis, herpes genital warts, herpes encephalitis, herpes meningitis, herpes bells palsy, atypical pain syndrome, trigeminal neuralgia, postinfectious encephalomyelitis, depending on severity, body part affected, or immunocompetent or impaired Treatment with antiviral agents such as oral Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, or Famciclovir depending on age |
|||
|
■ Herpes simplex virus infections (herpes febrile/fever blister/cold sore) are mainly caused by type 1 herpes simplex virus infection. |
||||
|
cause |
Herpes virus type 1 (HSV-1) or herpes type 2 virus (HSV-2) | |||
|
symptoms, signs |
Symptoms of herpes virus infection (herpes simplex virus infection) vary depending on the body part, the severity, the disease day, and the age. |
|||
|
diagnosis |
This disease can be easily diagnosed by combining the history, symptoms, and examination findings. Diagnosis is made by culturing the virus with blood pus or secretions in the affected area, or by performing a biopsy of the affected area or microscopic Tzanck Test. Differential diagnoses should be made with herpangina or pharyngitis (Herpangina), aphthous ulcer, hand, foot and mouth disease, and contact dermatitis. It can also be diagnosed by PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, and IgG antibody tests. |
|||
|
treatment, prevention |
Asymptomatic herpes infections are treated with observation. gingival stomatitis, early genital herpes, eczema herpes, immunodeficiency herpes, Herpes lip recurrent genital herpes, herpes conjunctival keratitis, herpes genital warts, herpes encephalitis, herpes meningitis, herpes bells palsy, atypical pain syndrome, trigeminal neuralgia, postinfectious encephalomyelitis, depending on severity, body part affected, or immunocompetent or impaired Treatment with antiviral agents such as oral Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, or Famciclovir depending on age |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
Recurrent herpes simplex lesion (recurrent herpes simplex virus infection or recurrent herpes) | |||
|
cause |
||||
|
symptoms and signs |
The symptoms are almost the same as the symptoms of early infection. |
|||
|
diagnosis |
This disease can be easily diagnosed by combining the history, symptoms, and examination findings. Diagnosis is made by culturing the virus with blood pus or secretions in the affected area, or by performing a biopsy of the affected area or microscopic Tzanck Test. Differential diagnoses should be made with herpangina or pharyngitis (Herpangina), aphthous ulcer, hand, foot and mouth disease, and contact dermatitis. It can also be diagnosed by PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, and IgG antibody tests. |
|||
| Prophylactic treatment with oral acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir. Because recurrent herpesvirus infection is caused by tiredness, menstruation, high tension, prolonged exposure to the sun, high fever, or other problems, harm as much as possible the triggers and prevent recurrence of recurrent herpesvirus infection. should be prevented | ||||
|
|
||||
|
Types of herpes virus infection |
Genital herpes simplex virus infection |
|
|
cause |
Herpes virus type 1 (HSV-1) or herpes type 2 virus (HSV-2). Recurrent genital herpes virus infection can be caused by herpes virus rehabilitation and reinfection. | |
|
symptoms, signs |
Puncture sores can develop on the vulva, perineum, or both in men or women. Most early genital herpes infections are asymptomatic. |
|
|
diagnosis |
This disease can be easily diagnosed by combining the history, symptoms, and examination findings. Diagnosis is made by culturing the virus with blood pus or secretions in the affected area, or by performing a biopsy of the affected area or microscopic Tzanck Test. Differential diagnosis should be made with herpangina or pharyngitis (Herpangina), aphthous ulcer, hand, foot and mouth disease, and contact dermatitis. It can also be diagnosed by PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, and IgG antibody tests. |
|
|
treatment, prevention |
Prophylaxis with oral Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, or Famciclovir. Because recurrent herpesvirus infection is caused by tiredness, menstruation, high tension, prolonged exposure to the sun, high fever, or other problems, harm as much as possible the triggers and prevent recurrence of recurrent herpesvirus infection. should be prevented |
|
|
Types of herpes virus infection |
neonatal herpes simplex virus infection |
|
|
cause |
Herpesvirus type 1 (HSV-1) or herpes type 2 virus (HSV-2) can cause this disease. Herpesvirus-infected women’s genitals can become infected during childbirth, and sometimes, the herpesviruses in the genitals of ectopic mothers spread upwards with or without amniotic membrane breakage and can infect babies born with the herpesvirus. It can also be transmitted from a herpes virus infection that spreads to the mouth or hands of parents or caregivers after birth. Rarely, an intrauterine fetus may become infected. |
|
|
symptoms, signs |
Disseminated infectious diseases can occur by infecting multiple organs. It infects the liver, lungs, skin, mouth, eyes, and central nervous system. CNS infection may occur without skin or topical herpesvirus infection. Sometimes the skin, eyes, or mouth can also become infected. Only local infections of the eyes, skin, or mouth may occur. When a newborn has a fever, pustules, abnormal cerebrospinal fluid examination, and convulsions, a presumptive diagnosis of central herpes infection can be made. The mortality rate is quite high, and recurrent dermatitis may occur in infants. It can develop at any time within 6 weeks after birth. |
|
|
diagnosis |
This disease can be easily diagnosed by combining the history, symptoms, and examination findings. Diagnosis is made by culturing the virus with blood pus or secretions in the affected area, or by performing a biopsy of the affected area or microscopic Tzanck Test. Differential diagnosis should be made with herpangina or pharyngitis (Herpangina), aphthous ulcer, hand, foot and mouth disease, and contact dermatitis. It can also be diagnosed by PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, and IgG antibody tests. |
|
|
treatment, prevention |
Treatment with vascular acyclovir. Neonatal ocular herpesvirus infection is treated with vascular Acyclovir + eye drops (1% trifluridine, 0.1% iododeoxyuridine, or 0.15% ganciclovir). The good effect of treatment with Pretelivir was reported. The NEJM 1/16/2014. |
|
|
Types of herpes virus infection |
Herpes simplex virus infection that occurs in children after a neonatal period or in adolescent children |
|
|
cause |
Herpesvirus type 1 (HSV-1) or herpes type 2 virus (HSV-2) infection can cause the following herpes virus infections. |
|
|
symptoms, signs |
• Asymptomatic herpes—The majority of early herpes virus infections in postnatal and adolescent children are asymptomatic.
• Neonatal herpes – Any newborn with a herpes virus infection is treated with vascular Acyclovir. Newborns with herpes viral encephalitis, dermatitis, eye infections, or mucosal infections are treated with Acyclovir. Diagnosis and follow-up treatment are performed using brain MRI, ultra-sound imaging, and cerebrospinal fluid examination. • Gingival stomatitis- It is caused by HSV-1 infection and is a common infectious disease among herpesvirus infections that occur after the neonatal period. Fever, hypersensitivity, submandibular lymph node enlargement, periodontal and oral mucosa ulceration occur. • Genital herpes – A genital herpes infection in adolescents or adults can cause blisters and sores on the genitals of women and men. In most cases, it may be asymptomatic. HSV-1 herpes virus infection or HSV-2 herpes virus infection. • Herpes eczema- When children with atopic dermatitis are infected with the herpes virus, eczema herpes develops, resulting in hemorrhagic scabs, pustules, and pitted pustules. • Immunodeficiency herpes – Severe local infections and disseminated systemic infections can occur. • Herpes of the lips – After a primary infection, it can remain as a latent infection for life. After the primary infection has cleared, HSV-1 herpes recurrent lip herpes infection may occur for various reasons. At this time, one or several pustules may form around the mouth, on the rosacea, or on the edge of the lips. These compresses are called cold sores or fever blisters in English. • Recurrent genital herpes-1 If recurrent genital herpes occurs and then heals and recurs, one, two or several pustules may appear in clusters on the penis, scrotum, vulva, cervix, buttocks, genitals, perineum, and groin. HSV-2 recurrent genital herpes infection in people with immunodeficiency is much more severe and recurrent, and once it occurs, the symptoms are long-lasting. And it’s hotter and more itchy. • Herpes conjunctival keratitis may occur primarily or may recur. • Hands with Herpes – One herpes poultice – several can occur on the tip of the finger. • Herpes encephalitis – Brain HSV-1 herpes virus infection in postnatal and adolescent children can cause encephalitis. Encephalitis that occurs at this time can occur either primary or recurrent. Fever, changes in consciousness, personality changes, convulsions, neuropathy, and coma may occur. And you can die. • Herpes meningitis is mainly caused by infection with the HSV-2 herpes virus. • Herpes Bell’s palsy, atypical pain syndrome, trigeminal neuralgia, and postinfectious encephalomyelitis can also result from herpes virus infection. |
|
|
diagnosis |
This disease can be diagnosed by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings. Diagnosis is made by culturing the virus with blood pus or secretions in the affected area, or by performing a biopsy of the affected area or microscopic Tzanck Test. It can also be diagnosed by PCR, EIA, DFA, ALT, and IgG antibody tests. Differential diagnoses should be made with herpanic or pharyngitis (Herpangina), aphthous ulcer, hand, foot and mouth disease, and contact dermatitis. |
|
|
treatment, prevention |
Asymptomatic herpes infections are treated with observation. gingival stomatitis, early genital herpes, eczema herpes, immunodeficiency herpes, Herpes lip recurrent genital herpes, herpes conjunctival keratitis, herpes genital warts, herpes encephalitis, herpes meningitis, herpes bells palsy, atypical pain syndrome, trigeminal neuralgia, postinfectious encephalomyelitis, depending on severity, body part affected, or immunocompetent or impaired Treatment with antiviral agents such as oral Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, or Famciclovir, depending on age and presence or absence. |
|
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Helicase- Primase Inhibitor Pretelivir for HSV- 2 Infection. 1/16/ 2014
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the
medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your
doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.