목 림프절 비대와 목 림프절염, Lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis in the neck
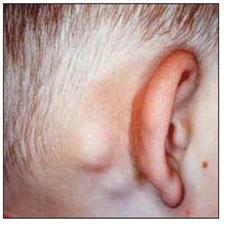
사진 3-21. 풍진으로 인해 귓바퀴 뒤 부위에 있는 두발의 가장자리 부위에 생긴 림프절 비대
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD. FAAP
- 여러 개의 림프절이 목에 있다. 그중 하나 또는 여러 개의 림프절이 비대되기도 하고, 림프절이 박테리아나 바이러스 등 병원체에 감염되어 림프절 감염병이 생길 수 있다(p.00~00 그림 1-13, 1-00, 1-00 참조).
- 두개강 내와 심장을 제외하고 전신 어디든지 림프절이 있다.
- 림프절은 메주콩알 만큼 크고 둥근 림프조직이다.
- 림프절은
-
- 혈액 속에 있는 죽은 세포, 백테리아, 바이러스, 노폐물을 처리해서 다시 피 속으로 배설 시키고
- 단백질을 흡수 배설하고,
- 항체를 생성하고
- 림프구를 생성하는 역할을 한다.
- 쓸데없는 백혈구를 걸러내고 면역체를 만들어 낸다.
- 신체 각 부위로 침입한 바이러스, 박테리아 또는 그 밖의 병원체가 신체 다른 부위로 더 이상 퍼지지 않게 방어하는 감염병 방어 기능을 갖고 있다.
- 알레르기성 질환을 일으킬 수 있는 항원이 콧구멍이나 구강 등을 통과해서 인체 다른 부위로 더 이상 들어가지 않도록 아데노이드와 편도는 방어 기능도 맡아 한다.
- 우리 몸속 곳곳에 퍼져 있는 많은 림프절 중 목이나 목 주위에 있는 림프절은 신체 다른 부위에 있는 림프절 보다 더 자주 박테리아에 감염되고 붓고 곪을 수 있다.
- 그 다음 겨드랑이와 가랑이에 있는 림프절이 더 자주 비대될 수 있고 잘 곪을 수 있다.
- 다음은 목에 있는 림프절 비대와 림프절염의 원인과 증상에 대해 설명한다.
| 목에 있는 림프절 비대와 림프절염의 원인 |
- A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균, 결핵균, 각종 바이러스, 곰팡이 등 병원체가 인두, 편도 등에 감염될 때, 또는 그런 병원체에 의해 목에 있는 림프절이 1차적으로 직접 감염될 때 목에 있는 림프절이 커지거나 림프절이 곪을 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제 8권 소아 청소년 호흡기 질환-A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균에 의한 감염병 참조.
- 인두염, 편도염, 인두 편도염, 구강염 등 소화기계 질병, 호흡기계 질병 및 상기도염을 일으킨 박테리아가 만들어낸 균독이 상기도 림프관과 구강 림프관을 통과하여 목에 있는 림프절에 퍼질 때 목에 있는 림프절이 반응하여 2차적으로 부을 수 있다.
- 알레르기성 질환을 일으킬 수 있는 해로운 항원이 구강 림프관이나 비강 속 림프관 또는 인두 속 림프관 등을 통과하여 몸속으로 점점 더 깊숙이 들어올 때 아데노이드와 편도와 목이나 신체 다른 부위에 있는 림프절이 반응하여 부을 수 있다.
- 전염성 단핵구증이나 그밖에 다른 여러 종류의 바이러스 감염병이 상기도에 있을 때 목에 있는 림프절이나 신체 다른 부위에 있는 림프절이 부을 수 있다.
- 부스럼, 아토피성 피부염, 지루성 피부염 등이 얼굴, 귓바퀴 뒤, 두피 등에 있거나, 그 부위에 곤충물림이 생기면 그 주위 림프절이 붓고 곪을 수 있다.
- 백혈병이 있을 때 악성 백혈구나 신체 다른 부위에 있는 악성 종양에서 나온 암세포가 목에 있는 림프절에 전이될 때 목에 있는 림프절이 붓을 수 있다.
- 묘소병(고양이 할큄병)이 있을 때 묘소병을 일으킨 박테리아가 목이나 가랑이, 겨드랑이 등의 림프절에 감염되어 림프절이 붓거나 곪을 수 있다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아 청소년 응급의료-고양이에게 물리거나 할퀴었을 때, 묘소병 참조).
- 알레르기성 비염이 있을 때는 아데노이드, 편도, 목에 있는 림프절이 붓을 수 있다.
- 가와사키병 등 비 감염성 질환 등으로 목 림프절이 부을 수 있다.
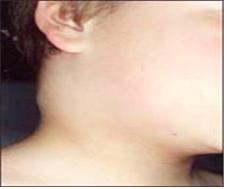
사진 2-1. 오른쪽 목 부위에 있는 림프절이 모소병으로 부었다. A군 연구균 편도염이나 인두염으로 목에 있는 림프절들이 사진에서 보는 것과 같이 부을 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
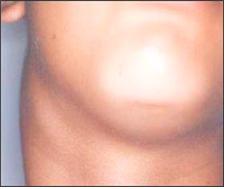
사진 2-2. 오른쪽 목 부위에 있는 림프절이 전염성 단핵구증으로 인해 부어 있다. A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 편도염이나 인두염으로 목에 있는 림프절들이 사진에서 보는 것과 같이 부을 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
| 목에 있는 림프절 비대와 림프절염의 증상 징후 |
- 신체 어는 계통의 어는 기관에 있는 림프절이 어느 정도로 부어 있느냐, 합병증의 유무, 림프절이 붓기만 했는지, 붓고 곪았는지, 림프절염이나 림프절 비대의 원인에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 아무 병도 없는 건강한 아이의 목부위에 있는 정상 림프절의 크기는 메주 콩알만큼 크다.
- 피부층 바로 밑 피하 조직에 정상적으로 있는 어떤 림프절은 피부층을 위쪽으로 밀고 불쑥 솟아 나와서 눈에 더 쉽게 띌 수 있다(사진 1-14 참조).
- 목이나 겨드랑, 사타구니 등의 림프절이 비대되고 곪을 때는 육안으로 쉽게 볼 수도 있고 만져 볼 수도 있고 아플 수도 있다(사진 2-1, 2-2 참조).
- 어떤 경우는 림프절이 밤알 크기만큼 커졌으나 만져도 아프지 않을 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 바이러스 감염병으로 부은 림프절은 손으로 만져도 많이 아프지 않고 많이 커지지도 않는다.
- 박테리아가 목에 있는 림프절에 직접 감염되어 그 림프절이 곪을 때는 전신이 아프고, 열이 나고, 곪은 림프절 바로 위에 있는 피부도 빨갛고 그 곪은 림프절을 만지면 심하게 아픈 것이 보통이다.
- 박테리아 감염으로 생긴 림프절염을 초기에 적절히 치료하지 않으며 그 림프절이 점점 더 붓고 완전히 곪아 고름이 잡힌다.
- A군 연구균에 감염되어 생긴 편도염이나 인두편도염을 앓을 때 그 박테리아 균독이 림프관을 통과해 턱 밑에 있는 목부위 림프절에 퍼질 때는 많이 붓고 아프다.
| 목에 있는 림프절 비대와 림프절염의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 진단할 수 있다.
- 편도염이나 인두염, 또는 인두편도염 등을 일으킨 A군 연구균이 만들어낸 균독이 목에 있는 림프절에 퍼질 때 림프절이 부을 수 있고, 그 박테리아가 목 림프절에 직접 감염되어 림프절이 붓거나 곪을 수 있다.
- 인두 점막층에서 점액을 면봉으로 조금 채취해서 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 박테리아 배양검사를 하든지, 항원과 항체 응집반응검사를 하든지, 또는 주사 바늘로 곪은 림프절에서 고름을 채취해서 박테리아 배양 검사를 해서 이 병을 확진할 수 있다.
- 이비 바이러스 인두편도염(전염성 단핵구증)이 있을 때는 목에 있는 림프절과 간과 지라 등이 동시 부을 수 있다.
- 전염성 단핵구증은 모노 테스트와 CBC 피 검사, 간기능 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다 [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제 8권 소아 청소년 호흡기 질환-전염성 단핵구 인두 편도염 참조.
- 결핵균이 목 림프절에 감염되어 목림프절이 부었거나 곪았을 때는 투베르쿨린 결핵 반응검사를 하고 가슴 X-선 사진, 곪은 림프절에서 고름을 채취한 후 결핵균 박테리아 검사를 하든지 곪은 림프절 전체를 떼어서 림프절 생체 조직검사를 해서 진단 치료한다.
- 묘조병으로 림프절이 붓거나 곪았을 때는 림프절에서 고름을 채취해서 박테리아 검사나 생체 조직검사를 하고 피에서 묘조병 항원과 항체검사를 해서 진단한다.
- 이상 여러 가지 진단 방법으로 목에 있는 림프절이 붓거나 곪은 원인을 확실히 알아낼 수 없는 때도 많다.
- 어떤 때는 이런 여러 종류의 검사를 하는 동시 의사의 처방에 따라 적절한 항생제로 10일 정도 치료하면서 그 병의 진행 상태를 관찰하며 추정 진단을 하고 그와 동시에 치료를 할 때도 있다.
- 드물지만 원인을 모르게 목 림프절이 심하게 붓고 곪았을 때는 림프절을 수술로 떼어 내고, 그 림프절 조직을 검사, 진단할 수 있다.
- 또 암 세포나 백혈병 등의 악성 백혈구가 림프절에 전이되어 목 림프절이 커질 수 있고 부을 수 있는데, 역시 필요한 피검사와 림프절 생체 조직 검사 등으로 이 병을 진단할 수 있다.
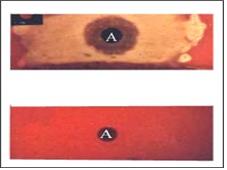
그림 2-3. 목 림프절이 부으면 인두점액으로 A군 연구균 박테리아 배양검사를 해 간접적으로 인두염이 A군 연구균 감염이 생겼고 목의 림프절도 인두염을 일으킨 A군 연구균의 균독으로 생겼다고 진단할 수 있다. 위 사진은 박테리아 배양검사 결과가 양성이고 아래는 음성이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
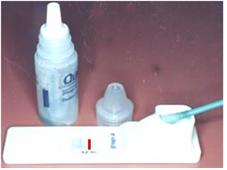
그림 2-4. 목의 림프절이 부으면 인두 점액으로 A군 연구균 항원 항체 응집반응으로 진단할 수 있다.목의 림프절이 A군 연구균 감염으로 인두염이 생겼고, 인두염을 일으킨 A군 연구균의 균독으로 목의 림프절이 부었다 추정진단 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
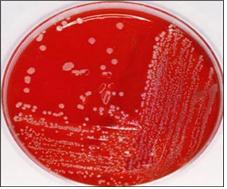
그림 2-5. 목 림프절이 붓고 고열이 나고 림프절이 분 원인을 확실히 모를 때는 혈액 박테리아 배양검사를 해서 진단할 수도 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
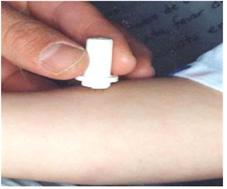
그림 2-6. 결핵균으로 인해 목 림프절이 붓고 염증이 생길 수 있다. TB 타인 테스트나 PPD 검사로 결핵성 림프절염을 진단할 수 있다
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
| 목에 있는 림프절 비대와 림프절염의 치료 |
- 림프절염과 림프절 비대의 원인, 정도, 증상 징후 등에 따라치료한다.
- 고열이 나고 목 림프절이 많이 붓고 심하게 아플 때는 병원에 입원해서 진단하면서 치료한다.
- 림프절염이나 림프절 비대의 원인을 찾는 동시 적절한 항생제 혈관주사 치료가 이상적 치료 방법이다.
- 목 림프절이 곪을 때는 림프절염 속에 들어 있는 박테리아나 그 밖의 다른 병원체가 그 곪은 림프절염이 있는 목 주위 심부로 쉽게 퍼져나갈 수 있다. 그 때문에 서둘러서 치료해야 한다.
- 두피나 얼굴 등이 할퀴거나, 곤충에 물려 생긴 상처에 박테리아가 감염되면 그 상처가 곪을 수 있다.
- 주위에 있는 목 림프절이 부을 때, 또는 바이러스 상기도염이나 다른 종류의 바이러스 감염병을 앓을 때 목 림프절이 커질 때는 그 바이러스 감염병이 점점 나아감에 따라 부었던 림프절도 저절로 낫는다.
- 전염성 단핵구증으로 커진 림프절은 항생제로 치료되지 않으나 자연히 낫는다.
- 결핵균으로 생긴 목 림프절염은 결핵 치료약으로 치료하면 잘 낫는다.
- 박테리아가 림프절에 감염되어 림프절이 조금 곪았을 때는 항생제로 치료하든지, 많이 곪았을 때는 곪은 림프절염을 수술로 제거하고 고름을 제거해 주는 동시 항생제로 치료한다.
- 고양이가 할퀴어 생긴 묘소병으로 커진 림프절이나 림프절염은 박트림 등으로 치료할 수 있고, 그대로 놓아두어도 자연히 낫는 경우도 있다.
- 드물게는 곪은 림프절염을 수술로 치료해서 곪은 림프절 전체를 제거 치료할 때도 있다.
Lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis in the neck

Picture 3-21. An enlarged lymph node at the edge of the head behind the pinna due to rubella Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD. FAAP
• Multiple lymph nodes in the neck. One or several of these lymph nodes may become enlarged, and the lymph nodes may become infected with pathogens such as bacteria or viruses, resulting in lymph node infection.
• Lymph nodes are located anywhere in the body except in the cranial cavity and the heart. • Lymph nodes are large and round lymphatic tissues as large as soybeans.
• Lymph nodes
o Processes dead cells, bacteria, viruses, and wastes in the blood and excretes them back into the blood
o Absorption and excretion of protein,
o to produce antibodies o It plays a role in the production of lymphocytes. o Filters out useless white blood cells and creates an immune system.
• It has an infectious disease defense function that prevents viruses, bacteria or other pathogens that have invaded each part of the body from further spreading to other parts of the body.
• Adenoids and tonsils also play a defensive function so that antigens that can cause allergic diseases do not pass through the nostrils or oral cavity and enter other parts of the body.
• Of the many lymph nodes spread throughout the body, the neck or the lymph nodes around the neck can become infected with bacteria, swell, and swell more frequently than lymph nodes in other parts of the body.
• Lymph nodes in the armpits and crotch may then become enlarged and more prone to stinging.
• The following explains the causes and symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and lymphadenitis. Causes of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and lymphadenitis
• When a pathogen such as group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, various viruses, and fungi infects the pharynx or tonsil, or when the lymph nodes in the neck are primarily directly infected by such pathogens, the lymph nodes in the neck enlarge or lymph nodes This can be [Parents should also become anti-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 8 Children and adolescents Respiratory diseases-Refer to Infectious diseases caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.
• Lymph nodes in the neck react when the mycotoxins produced by the bacteria that cause pharyngitis, tonsillitis, pharyngeal tonsillitis, stomatitis, etc. Thus, it can be poured secondarily.
• Adenoids and tonsils and lymph nodes in the neck or other parts of the body can react and swell when harmful antigens that can cause allergic reactions pass through the lymphatic vessels of the mouth, nasal passages, or the pharynx, etc., and enter more and more deeply into the body.
• Infectious mononucleosis or several other viral infections in the upper respiratory tract can cause swelling of lymph nodes in the neck or elsewhere in the body.
• If swelling, atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, etc. are present on the face, behind the pinna, or on the scalp, or if an insect bite occurs in those areas, the lymph nodes around them may become swollen and swollen.
• When you have leukemia When malignant white blood cells or cancer cells from a malignant tumor elsewhere in the body spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, the lymph nodes in the neck may swell.
• When there is cat’s disease (cat scratch disease), the bacteria that caused the cat’s disease can infect the lymph nodes in the neck, crotch, armpits, etc., causing the lymph nodes to swell or become swollen. -Volume 1, Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents-When bitten or scratched by a cat, see Graveyard Disease).
• If you have allergic rhinitis, your adenoids, tonsils, and lymph nodes in your neck may swell.
• Neck lymph nodes may swell due to non-infectious diseases such as Kawasaki disease.

Picture 2-1. A lymph node in the right neck area was swollen due to Moso disease. With group A research bacteria tonsillitis or pharyngitis, lymph nodes in the neck may swell as shown in the picture. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Photo 2-2. The lymph nodes in the right neck area are swollen due to infectious mononucleosis. With group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal tonsillitis or pharyngitis, lymph nodes in the neck may swell as shown in the picture. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Signs, Symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and symptoms of lymphadenitis
• Symptoms vary depending on the degree of swelling of the lymph nodes in the freezing system of the body, the presence of complications, whether the lymph nodes are only swollen, swollen, and swollen, and the cause of lymphadenitis or enlarged lymph nodes.
• A normal lymph node in the neck of a healthy child without any disease is as large as a soybean pea.
• Certain lymph nodes, normally in the subcutaneous tissue just below the layer of skin, may protrude upward by pushing the layer of skin upward, making them more visible (see Figures 1-14).
• When lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, groin, etc. are enlarged and swollen, they can be easily seen with the naked eye, touched, or painful (refer to photos 2-1 and 2-2).
• In some cases, the lymph nodes may be as large as chestnuts, but not painful to the touch.
• In general, swollen lymph nodes due to viral infections do not hurt too much and do not enlarge too much when touched.
• Bacteria directly infects the lymph nodes in the neck, and when the lymph nodes become sore, the whole body aches, there is a fever, the skin just above the swollen lymph nodes is red, and it is usually very painful to touch the swollen lymph nodes.
• Lymphadenitis caused by a bacterial infection is not treated properly in the early stages, and the lymph nodes become increasingly swollen, stagnant, and pus-filled.
• When you have tonsillitis or pharyngotonsillitis caused by infection with group A research bacteria, when the bacterial toxin passes through the lymphatic vessels and spreads to the lymph nodes in the neck area under the chin, it swells and hurts a lot.
Diagnosis of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and lymphadenitis
• Diagnosis can be made by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
• When the mycotoxins produced by the group A research bacteria that cause tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or pharyngotonsillitis spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, the lymph nodes may swell, and the bacteria may directly infect the lymph nodes in the neck, causing the lymph nodes to swell or become swollen.
• A small amount of mucus from the pharyngeal mucosa is collected with a cotton swab and cultured for group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus bacteria, antigen-antibody aggregation reaction test, or pus from a punctured lymph node and bacterial culture test can be confirmed.
• When you have rhinovirus pharyngotonsillitis (infectious mononucleosis), the lymph nodes in the neck and the liver and spleen may swell at the same time.
• Infectious mononucleosis can be diagnosed with a mono test, CBC blood test, liver function test, etc. [Parents should also become at least the haf-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Vol.
• If the neck lymph node is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the neck lymph node is swollen or shriveled, a tuberculin tuberculosis test is performed, chest X-ray, pus is collected from the swollen lymph node, and the tuberculosis bacteria is tested, or the whole swollen lymph node is removed and biopsied for lymph node biopsy. to diagnose and treat
• When the lymph nodes are swollen or stinged due to catholic disease, pus is collected from the lymph nodes, and a bacterial test or biopsy is performed, and the blood is tested for antigens and antibodies to the catholic disease. ]
• Abnormalities In many cases, the cause of swollen or stiff lymph nodes in the neck cannot be determined with various diagnostic methods.
• In some cases, these tests are performed simultaneously, and treatment is performed with an appropriate antibiotic for 10 days according to the doctor’s prescription, while observing the disease’s progression, making a presumptive diagnosis, and treating it at the same time.
• In rare cases, when the neck lymph nodes are severely swollen and swollen for unknown causes, the lymph nodes are surgically removed, and the lymph node tissue can be examined and diagnosed.
• In addition, malignant white blood cells such as cancer cells or leukemia may metastasize to the lymph nodes, causing the neck lymph nodes to enlarge and swell.

Figure 2-3. If the lymph nodes in the neck are swollen, a culture test of group A research bacteria can be performed with pharyngeal mucus to indirectly diagnose pharyngitis as group A research bacteria infection, and the lymph nodes in the neck are also caused by the mycotoxin of group A research bacteria that causes pharyngitis. The picture above shows a positive bacterial culture test, and the bottom picture is negative.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Figure 2-4. If the lymph nodes in the neck are swollen, the pharyngeal mucus can be diagnosed as an agglutination reaction with the group A research bacteria antigen-antibody. Swelling can be presumed to be diagnosed. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Figure 2-5. If the neck lymph nodes are swollen and have a high fever, and the cause of the swollen lymph nodes is not known for sure, a blood bacterial culture test may be used to diagnose it. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP

Figure 2-6. Mycobacterium tuberculosis can cause the neck lymph nodes to become swollen and inflamed. Tuberculous lymphadenitis can be diagnosed with the TB Tyne test or PPD test Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Treatment of enlarged lymph nodes and lymphadenitis in the neck
• Treat according to the cause, degree, and symptom signs of lymphadenitis and enlarged lymph nodes.
• If you have a high fever, a lot of swelling of the neck lymph nodes, and you are seriously ill, you should be admitted to the hospital for diagnosis and treatment.
• The ideal treatment method is to find the cause of lymphadenitis or enlarged lymph nodes, and at the same time, appropriate antibiotics and vascular injections.
• When the neck lymph nodes are sore, bacteria or other pathogens from the lymphadenitis can easily spread to the deep area around the neck where the sore lymphadenitis is located. That is why it must be treated promptly.
• If the scalp or face is scratched, or if a wound caused by an insect bite is infected with bacteria, the wound may become stagnant.
• When the surrounding neck lymph nodes swell, or when you have viral upper respiratory tract infections or other viral infections and the neck lymph nodes become enlarged, the swollen lymph nodes will heal on their own as the viral infection progresses.
• Lymph nodes enlarged by infectious mononucleosis are not treated with antibiotics, but will heal spontaneously.
• Neck lymphadenitis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be cured by treatment with tuberculosis drugs.
• If the lymph node is infected with bacteria and the lymph node is a little sore, treat it with antibiotics, or if the lymph node is very sore, the swollen lymphadenitis is surgically removed and treated with antibiotics at the same time to remove the pus.
• Lymph nodes or lymphadenitis enlarged due to a cat scratching disease can be treated with Bactrim, and in some cases, it will heal naturally even if left as it is.
• In rare cases, stasis lymphadenitis is treated with surgery to remove the entire stasis lymph node.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-본 사이트의 내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.”