신생아 괴사성 소장 결장염, Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis
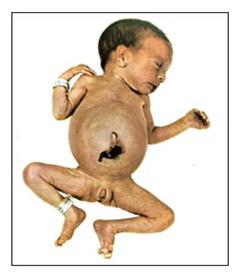
그림 315. 괴사성 소장 결장염으로 복부팽만이 생긴 미숙아
출처: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA와 소아가정간호백과
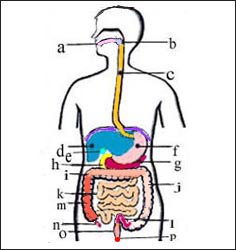
그림 2. 소화기계(소화계) 해부도
a-입, b-인두, c-식도, d-간, e-담낭, f-위, g-췌장, h-십이지장, i-횡행결장, j-하행결장, k-소장, l-S상결장,
m-상행결장, n-충수, o-직장, p-항문
Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
신생아의 소장관과 결장관에 생기는 괴사성 장염을 신생아 괴사성 소장결장염이라고 한다.
- 미 신생아 집중 치료실에서는 약 1~5%의 발생률을 볼 수 있다(출처; Consultant for Pediatricians, February 2004, p.61).
- 소장과 결장의 점막층에 손상이 맨 먼저 생기고 그 손상을 통해서 박테리아 감염이 소장관과 결장관에 생기고 그 장관 벽에 기종이 생길 수 있다.
- 처음에는 기종이 점막층 하조직에 생기고 그 다음에는 장벽의 근육층 그리고 장막층에도 생길 수 있다.
- 그리고 일레우스(Ileus)가 생길 수 있고 그 부분의 장벽이 괴사되고 심하면 장벽이 천공될 수 있다.
- 그에 따른 여러 가지 위중한 합병증과 증상 징후가 생길 수 있는 매우 위중한 신생아 원인 불명의 병이다.
- 장관 내 세균이 비정상적으로 과다로 증가되고 장관 내에 가스가 차고 복강이 팽만하고 심한 점액성 설사 또는 혈액성 설사를 동반한다.
- 이런 병변이 때로는 위에도 생길 수 있다.
- 출생 체중이 1,500 그램 이하 되는 저체중 미숙아에게 더 잘 생길 수 있으나 만삭에 태어난 정상 체중 신생아에게도 생길 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 생후 14일 이내 신생아에게 이 병이 더 생길 수 있으나 드물게 생후 5주 이전 신생아나 영아에게도 생길 수 있다.
- 어려운 분만으로 태어난 신생아, 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군, 저 아프가 점수, 저산소증, 저 체온증, 저혈당증, 조기 영양공급, 패혈증, 교환 수혈, 약물 치료, 질식, 제대혈관 카테터 삽입치료, 호흡곤란, 고 삼투압 인공영양 치료 등의 병력이 있었던 신생아에게 이 병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 어떤 종류의 선천성 심장기형이 있는 신생아에게는 이 병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다고 한다.
- 경구용 인공영양 피딩이나 감염 등으로 이 병이 생길 수 있다.
| 신생아 괴사성 소장 결장염의 증상 징후 |
- 보통 생후 2주 내 생긴다.
- 경미할 때는 소화불량으로 생기는 증상 징후와 비슷할 수 있다.
- 심할 때는 무호흡증, 서맥, 저체온, 기민상태, 신경과민, 담즙 섞인 구토, 피 섞인 구토, 복부 팽만, 혈변과 심한 설사, 위 팽만 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있고 그런 증상 징후가 점점 더 심해 질 수 있다.
- 복벽이 홍색으로 변화될 수 있고 부을 수 있다.
- 잘 먹지 않고 저혈압, 저 체온, 창백, 호흡곤란 등 증상 징후가 생길 수 있고 쇼크에 빠질 수 있다.
- 혈소판 감소증으로 자반증이 생길 수 있다.
| 신생아 괴사성 소장결장염의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰 등을 종합해서 진단할 수 있다.
- 소변검사, 대변검사, 뇌척수액 검사, CBC 피 검사를 한다.
- 소변, 대변, 혈액, 뇌척수액 등으로 세균검사, 가슴 복부 X선 사진검사, 복부 초음파 검사, MRI 검사로 진단한다.
| 신생아 괴사성 소장 결장염의 치료 |
- 경구를 통한 영양공급을 일시적으로 중단하고 혈관 수액공급, 전해질 공급, 영양공급으로 치료한다.
- 산소호흡 치료,
- 적절한 항생제(보통 Ampicillin, Gentamicin과 Clindamycin)로 치료한다.
- 인간 생명 보존 지지 치료, 구위 피딩 튜브 삽입 위액제거치료를 한다.
- 필요에 따라 혈소판 수혈, 및 혈액수혈 등으로 치료하기도 한다.
- 기도 내관 삽입 호흡치료도 하고 진통제 치료를 할 수 있다.
- 80%는 내과적으로 치료하고 나머지는 필요에 따라 적절한 외과적으로 치료한다.
- 외과적 치료 후 생존율은 약 44~87%이다.
- Probiotics제로 이 병을 예방할 수 있다(Contemporary Pediatrics June 2007).
| Update 2/20/2022
조산으로 태어난 영아들의 사망의 주 원인들 중 괴사소장 대장염(Necrotizing enterocolitis)이나 패혈증은 큰 원인들이다.조산으로 태어난 영아들의 장내에 있는 상존 세균에 불균형이 생긴다. 그로 인해 괴사소장 대장염이 생긴다고 믿는다, 그래서 Probiotics을 공급하면 괴사소장 대장염 등을 예방 할 수 있다고 한다. 그러나 probiotis, prebiotics. synviotics 의 효과의 차이를 확실히 모른다. Pediatrics.1/2021 Update 2/20/2022 Necrotizing enterocolitis and sepsis are the major causes of death among infants born prematurely. An imbalance occurs in the intestinal bacteria of infants born prematurely. It is believed that this causes necrotizing small intestine colitis, so it is said that supplying probiotics can prevent necrotizing small intestine colitis. But probiotics, prebiotics. It is not sure about the difference in the effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Pediatrics.1/2021 |
Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis

Figure 315. Premature infant with bloating due to necrotizing enterocolitis Source: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing

Figure 2. Digestive system (digestive system) anatomy a – mouth, b – pharynx, c – esophagus, d – liver, e – gallbladder, f – stomach, g – pancreas, h – duodenum, i – transverse colon, j – descending colon, k – small intestine, l – sigmoid colon, m – ascending colon, n – appendix, o – rectum, p – anus Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Necrotizing enterocolitis in the small intestine and colon in newborns is called neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis.
• In neonatal intensive care units, the incidence is about 1-5% (source; Consultant for Pediatricians, February 2004, p.61).
• Damage to the mucous membranes of the small intestine and colon is the first to occur, through which bacterial infection can develop in the small intestine and colon and emphysema of the intestinal wall.
• Emphysema may initially develop in the submucosal tissue, then in the muscular and serous layers of the intestinal wall.
• And Ileus may occur, and the barrier in that area may be necrotic and, in severe cases, the barrier may be perforated.
• It is a very serious neonatal disease of unknown etiology that can cause many serious complications and symptoms.
• Abnormally increased bacteria in the intestinal tract, accompanied by gas in the intestinal tract, bloating of the abdominal cavity, and severe mucinous or bloody diarrhea.
• These lesions can sometimes also develop in the stomach.
• It is more likely to occur in low birth weight premature infants weighing less than 1,500 grams, but may also occur in normal weight newborns born at full term.
• The disease is more common in newborns within the first 14 days of life, but rarely in newborns or infants before the age of 5 weeks.
• Newborns born with difficult delivery, idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome, low Apgar score, hypoxia, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, premature nutrition, sepsis, exchange transfusion, medication, asphyxiation, umbilical cord catheterization, dyspnea, hyperosmotic artificial Newborns with a history of nutritional therapy are more likely to develop the disease.
• Newborns with some type of congenital heart anomaly are said to be more prone to the disease.
• This disease can be caused by oral artificial nutrition feeding or infection.
Symptomatic signs of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis
• Usually occurs within the first 2 weeks of life.
• When mild, the symptoms may resemble signs of indigestion.
• In severe cases, symptoms such as apnea, bradycardia, hypothermia, alertness, nervousness, biliary vomiting, bloody vomiting, abdominal distension, bloody and severe diarrhea, and stomach bloating may occur, and these symptoms may become more severe. have.
• The abdominal wall may turn red and may swell.
• If you do not eat well, you may experience symptoms such as low blood pressure, low body temperature, paleness, difficulty breathing, and you may fall into shock.
• Thrombocytopenia can cause purpura.
Diagnosis of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis
• Diagnosis can be made by combining medical history, symptoms, and examination.
• Urine test, stool test, cerebrospinal fluid test, CBC blood test.
• Diagnosis is made with urine, feces, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. bacteriological examination, chest X-ray examination, abdominal ultrasound examination, and MRI examination.
Treatment of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis
• Temporarily discontinue oral nutrition and treat with vascular fluid supply, electrolyte supply, and nutritional supply.
• oxygen breathing therapy;
• Treat with appropriate antibiotics (usually Ampicillin, Gentamicin and Clindamycin).
• Human life-saving supportive therapy, orgastric feeding tube insertion, gastric juice removal therapy.
• If necessary, platelet transfusions and blood transfusions are used for treatment.
• Airway endotracheal tube insertion breathing therapy and analgesic therapy are available.
• 80% are treated medically and the rest are treated surgically as needed.
• The survival rate after surgical treatment is about 44-87%.
• Probiotics can prevent this disease (Contemporary Pediatrics June 2007).
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-본 사이트의 내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.”