유방 농양, Breast abscess
-
유방에 국소적으로 생긴 박테리아(세균성) 감염병을 유방 내 고름주머니 또는 ‘유방 농양’이라고 한다.
-
유방 농양은 유방 속 깊숙이 있는 유방조직에 생기는 박테리아 농양이다.
-
유방 농양은 젖을 먹이지 않는 여성의 유방에게도 생길 수 있다. 그러나 모유 수유 하는 여성에게 더 잘 생긴다. 특히 빈혈이 있거나 박테리아 감염에 대한 저항력이 약한 수유모일수록 발병 확률이 더 높다.
-
젖꼭지가 갈라지거나 젖꼭지 염증이 생기면 박테리아 유방염이 더 잘 발생될 수 있다. 이 박테리아 유방염에 농(고름)이 잡혀 유방 농양이 된다.
-
유방 농양은 분만 후 젖을 먹이는 산모의 유방에 언제든지 생길 수 있다. 그러나 분만 후 젖을 먹이기 시작한 2~6주 이내에 더 잘 발병될 수 있다.
-
박테리아 감염성(세균 감염성) 유방염을 조기에 적절히 치료하지 않거나 잘못 치료하거나 치료가 잘되지 않거나 늦게 치료 할 때 세균 감염성 유방염에 농양이 잡히고 유방농양이 생길 수 있다.
-
박테리아 감염성 유방염을 항생제로 치료한지 2~3일이 지났는데도 확연히 치료가 되지 않으면 유방 농양이 있는지 일단 의심해야 한다.
-
박테리아 감염성 유방염과 유방 농양의 주된 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
-
박테리아 감염성 유방염의 전형적인 증상 징후는 피곤하고 권태감이 생기며 미열 내지 고열이 나고 한전, 구토 등의 증상 징후가 나타나는 것이다.
-
거기에 농양이 생기면 유방이 국소적으로 붓고 붉어지고 그 부위를 손으로 만지거나 그 쪽 유방에서 나오는 젖을 먹이면 몹시 아플 수 있다. 또, 그 쪽 유방 부위를 만지면 고름주머니가 만져진다.
-
박테리아 감염성 유방염만 있는 유방에서 분비되는 젖은 아기에게 계속 먹일 수 있다. 그러나 유방 농양이 있는 박테리아 감염성 유방에서 분비되는 젖을 아기에게 먹여서는 안 된다.
-
수술로 유방 농양을 배농해 다 나을 때까지 모유 수유를 일단 중단해야 할 때도 있다. 그와 동시에 유방 농양이 있는 쪽 유방에 괴여 있는 젖을 유축기로 짜서 버리고 적절한 항생제로 치료해야 한다.
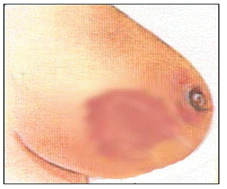
그림 4-16. 유방에 생긴 유방농양
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그림 4-17. 유방 농양이 생기면 그 쪽 유방이 아프고 한전이 나고 고열 증상이 나타날 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
|
다음은 “젖몸살, 유방염, 혼합수유, 유방농양”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 젖몸살, 유방염, 혼합수유, 유방농양
Q.
안녕하세요. 저는 첫 아이 때 출산 후 젖몸살을 심하게 했습니다. 모유가 많아서, 한편으론 걱정을 안 했지만 너무 아파서요. 유축기를 구입해 사용하면 괜찮을까요? 또, 둘째아이에게 수유할 때는 모유의 양이 줄어들 수가 있다고 하여 혼합수유를 할까 싶은데요, 어떤 점에 유의해야 될까요? 감사합니다.
A.
-
산모님, 안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. ‘젖몸살’이란 말은 아주 오래 전부터 써왔지만 표준 의학용어는 아닌 줄 압니다.
-
제가 알기로는 박테리아가 유방에 감염되어 세균 감염성 유방염이 생기고, 열이 나고, 유방과 전신이 아픈 증상을 동반하는 세균 감염성 유방염을 젖몸살이라고 했던 같습니다.
-
세균 감염은 없지만, 유방 내에 있는 모유생성 분비관계가 원활하게 기능하지 않아 젖이 흘러가는 유관이 막혀 생기는 유방 과잉 충만을 젖몸살이라고 합니다.
-
여기서는 세균 감염성 유방염(Infection mastitis)에 대해 말씀드리겠습니다.
-
갈라진 젖꼭지, 젖이 흘러나오는 젖샘관(유관)이 막히면 유방에 세균 감염성 유방염이 생기기 쉽습니다.
-
너무 조이게 브라를 입든지, 모유 수유를 제 때에 하지 않아 젖이 너무 많이 불었다거나, 스트레스나 피로를 너무 많이 받았다거나 하면 세균 감염성 유방염이 생기기 쉽습니다.
-
세균 감염성 유방염을 일으키는 박테리아에는 B군 연쇄상구균 등이 있습니다.
-
세균 감염성 유방염이 생겨 증상 징후가 시작되면 의사의 진단을 바로 받고 적절한 항생제로 적절히 치료해야 합니다. 이런 젖몸살은 비교적 쉽게 치료될 수 있습니다.
-
다음과 같이 치료합니다.
-
먼저 육체적으로 편히 누워 쉬어야 합니다.
-
가능한 한 모유 수유를 중지하지 말고 더 자주 모유 수유를 해서 젖이 유방 속에 고이지 않게 하는 것도 중요합니다.
-
모유 수유를 중단하거나 제대로 하지 않으면 세균 감염성 유방염이 유방 농양으로 이어질 수 있기 때문입니다.
-
세균 감염성 유방염이 있을 때 유선(포상샘)과 젖샘관(유관)에는 세균감염이 생기지 않는 것이 보통이기 때문에 모유 속에는 박테리아가 감염되어 있지 않습니다.
-
염려하시지 말고 모유 수유를 계속하십시오.
-
모유 수유를 하기 전이나 모유 수유를 하는 사이사이에 유방 더운찜질을 하시되, 한 번에 15~20분 동안 충분히 하십시오.
-
모유 수유는 2시간마다 하는 것이 좋습니다.
-
브라는 가능한 한 입지 마시고, 수분섭취를 충분히 하십시오.
-
열이나 통증이 있으면 타이레놀이나 모트린으로 치료하고 진통을 없애주세요.
-
아기에게 아구창이 있거나 엄마의 젖꼭지에 곰팡이 감염이 있으면 항 곰팡이감염 치료제로 적절히 치료하십시오.
-
세균 감염성 유방염을 잘 일으킬 수 있는 조건이 생기지 않도록 유방관리를 잘 하시면 세균 감염성 유방염은 잘 생기지 않습니다.
-
그렇다고 모든 수유모에게 세균 감염성 유방염이 꼭 생긴다고는 할 수 없으므로 미리부터 걱정을 하실 필요도 없습니다.
-
마지막으로 모유를 아기에게 주는 것은 아기에게도 좋지만 엄마, 아빠, 가족 모두에게 좋다고 생각합니다. 소아청소년과 의사 생활을 몇 10년 하다보면 인공영양을 먹은 아기들이 더 자주 병을 앓는 모습을 보게 됩니다. 여러 모로 모유는 아기에게 가장 좋은 음식물입니다. 그러니 될 수 있는 대로 모유만 먹이십시오.
-
‘혼합수유’란 말은 최근에 나온 말입니다. 소아청소년과 전문의들은 이 말을 쓰지 않습니다. 젖을 짜는 기구(유축기)에는 여러 종류가 있습니다. 그 중에서 Engell 전기 젖 짜는 유축기의 효능이 아주 좋습니다. 젖
-
을 꼭 짜내야 할 경우에는 젖을 손으로 우선 짜보시고 안 되면 유축기를 이용해 젖을 짤 수 있습니다.
-
모유 분비량은 수유모의 정신적․육체적 건강 상태와 균형 잡힌 음식물을 얼마나 잘 섭취하느냐 등에 따라 많이 좌우됩니다.
-
또, 수요 공급 법칙에 따라 적게 또는 많게 분비됩니다.
-
다시 한 번 말씀드리지만 수유모가 정신적․육체적으로 충분히 쉬고 음식물을 충분히 섭취하면 한 두 아기를 동시 키울 수 있을 정도로 모유가 충분히 분비됩니다.
-
질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
◘ 신생아 유방염(신생아 젖유종) The breast abscess of newborn infants
사진 88. 신생아의 유방염(젖유종) Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
|
Breast abscess
• Bacterial (bacterial) infections that occur locally in the breast are called pus sacs in the breast or “breast abscesses”.
• A breast abscess is a bacterial abscess that develops in the breast tissue deep inside the breast.
• Breast abscesses can also develop in the breasts of non-lactating women. However, it is more likely to occur in women who are breastfeeding. In particular, breastfeeding mothers with anemia or with poor resistance to bacterial infection are more likely to develop the disease.
• Cracked nipples or inflamed nipples are more likely to develop bacterial mastitis. This bacterial mastitis collects pus (pus) and becomes a breast abscess.
• A breast abscess can develop in the breast of a nursing mother at any time after delivery. However, it may be more likely to develop within 2 to 6 weeks of breastfeeding after delivery.
• Bacterial-infectious mastitis can become abscessed and develop breast abscesses if not treated early, properly, incorrectly, poorly or late.
• If there is no clear treatment for bacterial-infectious mastitis after 2 or 3 days of treatment with antibiotics, the presence of a breast abscess should be suspected.
• The main symptomatic signs of bacterial infectious mastitis and breast abscesses are:
• Typical symptom signs of bacterial infectious mastitis are fatigue, malaise, low to high fever, fever, and vomiting.
• If there is an abscess there, the breast becomes locally swollen and red and can be very painful if you touch the area or feed from that breast. Also, if you touch the breast on that side, you can feel the pus bag.
• You can continue to feed babies with milk from breasts with only bacterial infective mastitis. However, you should not feed your baby with milk from a bacterially infected breast with a breast abscess.
• Occasionally, you may need to stop breastfeeding until surgery has drained the breast abscess and has cleared up. At the same time, the milk accumulated in the breast on the side with the breast abscess should be pumped out and treated with appropriate antibiotics.

Figure 4-16. breast abscess in the breast Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 4-17. When a breast abscess occurs, the breast on that side may be sore, and symptoms of high fever may appear. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
The following is an example of a Q&A on health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “mammary glands, mastitis, mixed lactation, and breast abscess”. Q&A.
Breast tenderness, mastitis, mixed lactation, breast abscess
Q. Hello. When I was my first child, I had severe breast tenderness after giving birth. I have a lot of breast milk, so I wasn’t worried on the other hand, but it hurts so much. Is it okay to buy a breast pump and use it? Also, when I am breastfeeding my second child, I would like to mix breastfeeding because the amount of breast milk may decrease. What should I pay attention to? thank you.
A.
• Mother, hello. Thanks for the nice question. The term ‘mildew’ has been around for a very long time, but I know it’s not a standard medical term.
• As far as I know, Bacterial Infectious Mastitis, which is caused by a bacterial infection of the breast, which is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, breast and body aches, was referred to as mastitis.
• Although there is no bacterial infection, breast milk production and secretory system in the breast do not function well and the ducts through which milk flows are blocked.
• Here we are talking about infection mastitis.
• Cracked nipples and clogged ducts (ducts) from which milk flow are more likely to cause bacterial infection of the breast.
• Bacterial mastitis is more likely to occur if you wear a bra that is too tight, breastfeeding is not done on time, you have gained too much milk, or if you are stressed or tired too much. • Bacteria The bacteria that cause infectious mastitis include group B streptococci.
• If bacterial mastitis develops and symptoms begin to appear, it should be diagnosed by a doctor immediately and treated appropriately with appropriate antibiotics. These breast lumps can be treated relatively easily.
• Treat as follows.
• You must first lie down physically and rest.
• It is also important not to stop breastfeeding as much as possible, but also to breastfeed more often so that milk does not accumulate in the breast.
• If breastfeeding is stopped or not done properly, bacterial mastitis can lead to a breast abscess.
• When you have bacterially infectious mastitis, there is no bacterial infection in your breast milk because bacterial infections usually do not occur in the mammary glands (acinar glands) and mammary glands (mammary ducts).
• Don’t worry and continue breastfeeding.
• Apply warm breast compresses before or between breastfeeding, but enough for 15 to 20 minutes at a time.
• It is recommended to breastfeed every 2 hours.
• Avoid wearing bras as much as possible, and drink plenty of water.
• If you have fever or pain, treat it with Tylenol or Motrin and relieve the pain.
• If your baby has thrush or has a fungal infection in the mother’s nipples, treat it appropriately with antifungal medications.
• If you take good care of your breasts so that conditions that can easily cause bacterial infection mastitis do not arise, bacterial infection mastitis is unlikely to occur.
• This does not mean that all breastfeeding mothers will develop bacterial mastitis, so there is no need to worry in advance.
• Finally, I think breastfeeding your baby is good for your baby, but it’s good for you, your dad and everyone in your family. After a few ten years of working as a pediatrician, you will see that babies who have been given artificial nutrition get sick more often. In many ways, breast milk is the best food for babies. So, only breastfeed if possible.
• The term ‘mixed feeding’ is a recent term. Pediatricians do not use this term. There are several different types of expressing devices (pumps). Among them, the efficacy of the Engell electric milking pump is very good. milk
• If it is absolutely necessary to express the milk by hand, you can express it by hand first.
• The amount of milk produced depends a lot on the mother’s mental and physical health and how well she eats a well-balanced diet.
• Also, less or more is secreted according to the law of supply and demand.
• Again, if a nursing mother is sufficiently mentally and physically rested and consuming enough food, breast milk is secreted enough to support one or two babies at the same time.
• If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact us. thank you. Lee Sang-won, M.D
◘ The breast abscess of newborn infants
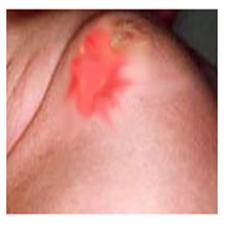
Photo 88. Mastitis in newborns . Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Bacterial infection in a localized area of a newborn’s breast can cause the breast to become stuffy and collect pus.
• This localized breast infection is called neonatal mastitis or neonatal lactoma.
• Touching or squeezing a newborn’s breast with unclean hands can lead to bacterial infection of the breast.
• Occasionally, a newborn’s breast may swell spontaneously for no apparent reason.
• It was customary to pull the nipples of newborn girls by hand to prevent the development of the inverted nipples that adult women may have. Such a bad habit can lead to lactation.
• Staphylococcus aureus, group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, Escherichia coli, or other bacterial infections can cause mammary glands ([Parents should also become at least the half-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Vol. 25 Pregnancy, delivery, and newborns Caring for – see Mastitis (mastitis)). Signs of symptoms of mastitis (lactoma) in newborns
• Symptoms vary depending on the type of bacteria causing the mastitis and the severity of the mastitis.
• When a newborn’s breasts are stale, the breasts are red, swollen, and painful.
• If it is not treated promptly at this time, mastitis may worsen and severe stinging may occur.
• The pus can collect and cause a high fever, which can lead to sepsis and life-threatening. Treatment of mastitis (lactoma) in newborns
• Do not touch the breast of a newborn baby with unclean hands.
• Once the breasts are sore from mastitis, emergency treatment with appropriate antibiotic injections is essential.
]• If you have a high fever while suffering from lactoma, you should be treated immediately with an intravenous antibiotic in the hospital.
• When pus is collected in the lactoma, the pus must be removed surgically.
• When a newborn’s breast is normally enlarged, do not touch or express the enlarged breast with unclean hands.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.