항생제(항생물질/항균제)와 항생제 치료에 관한 백문백답, Antibiotics and 100 Qs & As on antibiotic treatments
항생제(항생물질/항균제)
-
박테리아 감염병을 치료할 때 그 감염
-
병을 일으킨 박테리아를 죽여 박테리아 감염병을 치료할 수 있는 항생제와 박테리아가 체내에서 더 이상 증식할 수 없게 해서 박테리아가 결국에는 다 죽어 감염병이 낫게 하는 약물을
-
통틀어 항생제, 항균제, 또는 항생물질이라고 한다.
-
항생제에는 여러 형태로 제조된다.
-
액체형태 항생제,
-
가루형태 항생제,
-
캡슐형태 항생제,
-
알형태 항생제(정제),
-
점적형태 약제(방울 약),
-
근육 주사형태 항생제,
-
혈관 주사형태 항생제,
-
질 강 속이나 항문 속에 넣어 치료할 수 있는 좌약형태
-
피부, 눈, 귓구멍 속이나 콧구멍 속 등에 넣을 수 있는 점적형태 항생제도 있다.
-
비강 속이나 구강 속에 뿌릴 수 있는 분무제 형태 항생제,
-
기도 속으로 흡인할 수 있는 항생제 분무형태 제도 있다.
-
피부나 점막 등에 바르는 연고, 크림 형태 등의 항생제도 있다. 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과–제 21권 소아청소년 가정간호–약물과 약물형태 참조. 항생제(항균제)의 분류, 항생제 종류, 항생제 일반 명, 항생제 상품명, 항생제 투약경로, 항생제의 보통 용량, 항생제 투약 간격 참조
-
-
항생제의 종류에는 수백 종류가 있고 감염병을 일으킨 박테리아의 종류, 박테리아의 내성의 유무에 따라 (항생물질 저항성 또는 항생물질 내성 유무), 감염병의 종류와 중증도, 환아의 나이, 항생제에 부작용의 유무, 알레르기 유무 등의 병력에 따라 적절한 항생제를 선택해서 감염병을 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
-
세팔로스포린(Cephalosporins)계 항생제 등 광범위 항생물질,
-
에스토마이신(Erythromycin),
-
클라리스로마이신(Clarithromycin), 아지트로마이신(Azithromycin) 등과 같은 항생물질은 마크롤라이드계 항생물질,
-
살균성 항생물질 등으로 항생제를 분류하기도 한다.
-
-
어떤 감염병을 치료할 때 그때그때의 상황에 따라 치료를 시작하기 전에 세균검사를 하지 않고 경험적으로 항생제 치료를 시작하기도 한다.
-
그러나 그람 염색 현미경 검사, 세균 배양 검사와 항생제 감수성 검사에서 얻은 결과에 따라 항생제를 선택해서 치료하는 방법이 가장 이상적인 감염병 치료이다.
-
그러나 여러 가지 이유로 세균검사를 하지 않고 감염병을 치료할 때가 많다.
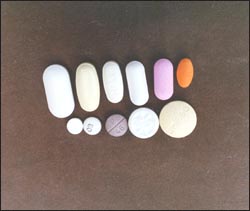
사진 1-12.여러 가지 크기와 모양으로 항생제 정을 만든다.
일반적으로 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들의 감염병을 치료할 때 그들은 알약(정) 항생제를 복용하기 곤란해 부적절하다.
알약을 깨트려 가루로 만들어서 복용할 수 있지만 그런 방법으로 알약을 투여하는 것은 부적절할 때가 많다.
알약이나 캡슐로 된 약을 깨트려 복용해야 할 때는 처방해준 의사나 약사에게 일단 문의해서 그
의 지시에 따라 복용한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
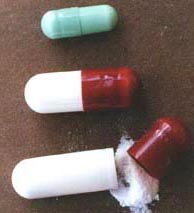
사진 1-11 캡슐로 제조된 항생제도 있다. 이런 종류의 항생제는 영유아들이나 일부의 학령기 아이들이 복용하기가 불편하기 때문에 그들에게 처방해 주지 않는 것이 보통이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 1-13. 항생제 좌약으로 감염병을 치료할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 1-14. 항생제 연고로 피부 감염병을 치료할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 1-15.환아의 나이, 항생제의 종류, 환부, 감염병이 얼마나 경미한지 또는 위중한지, 가정 환경 등에 따라 주사약, 물약, 알약, 고약, 좌약 등의 형태로 된 항생제 중 한두 가지를 선택해 그 항생제로 치료할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 1-16.요즘도, 감염병을 치료할 때 경구로 복용할 수 있는 가루 형태로 만든 항생제도 있다.
그러나 그 가루 형태의 항생제를 그냥 복용해 감염병을 치료하지 않고 가루형태 항생제를 복용하기 바로 전에 물에 타서 복용하는 것이 보통이다.
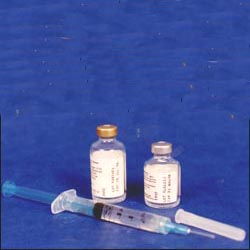
사진 1-18. 뇌막염, 패혈증 등 생명을 위협하는 위중한 감염병, 환아의 나이, 감염병의 종류, 치료상 문제, 항생제의 종류 등을 고려해서 항생제 정맥주사로 감염병을 치료하던지, 항생제 근육주사 등으로 치료할 수 있다.
점염병을 여러 번 주사 놓아 치료하면, 특히 소아들은 주사 맞아 치료 받기를 두려워하고 주사 맞을 때 아프기 때문에 주사로 치료받기를 아주 싫어한다.
또 성인들도 소아들과 마찬가지로 여러 번 주사를 맞아 치료받는 것을 아주 싫어한다.
요즘, 국소 마취제를 주사 맞기 전에 주사 맞을 국소에 바르든지 뿌릴 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
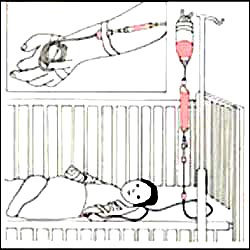
그림 1-17. 환아의 나이, 신체 어느 국소에 감염병이 생겨 있나, 뇌막염이나 패혈증, 또는 농가진 등 감염병의 종류, 감염병을 일으킨 병원체의 종류, 항생제의 종류, 치료 중 야기될 수 있는 문제와 상황 등을 참작해 항생제를 정맥주사로, 근육주사로, 경구로, 또는 그 외 다른 투여 경로 중 가장 적절한 투여 경로를 선택해 감염병을 치료하는 것이 원칙이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
항생제 치료에 관한 백문 백답
One hundreds of questions and answers on antibiotic treatments
Q.
전신 감염병(전신성 전염병)에 걸렸을 때 전신성 박테리아 감염병(전신성 세균성 감염병)인지 전신성 바이러스 감염병(바이러스 감염병)인지 어떻게 구별 하나요.
A.
대부분의 경우, 전신 감염병의 증상 징후 등을 참작해 임상적으로 확실히 구별하기가 어렵다.
특히 전신 감염병의 초기에는 세균 검사 등을 하지 않고 임상적으로 확실히 감별진단하기가 더 어렵다.
일반적으로 전신성 박테리아 감염병이 있을 때는 열이 더 난다든지 더 심하게 앓는 것이 보통이다.
그러나 어떤 전신성 바이러스 감염병을 앓을 때도 고열이 날 수 있고 아주 심하게 앓을 수 있고 증상 징후도 심하게 나타날 수 있다.
그 때문에 전신성 박테리아 감염병을 앓고 있는지 또는 전신성 바이러스에 감염병을 앓고 있는지, 특히 발병 초기에는 확실히 쉽게 감별 진단하기가 어려운 때가 많다.
그런 이유로 전신 감염병을 앓을 때는 이 두 종류의 병원체 중 어떤 종류의 병원체에 감염되어 있는지 감별 진단을 속히 받는 것이 중요하다.
참고로 대개의 경우, 전신성 심한 박테리아 감염병을 앓을 때는 환아가 독성상태에 있는 것이 보통이고
전신성 바이러스 감염병을 앓을 때는 환아가 웃기도 하고 그렇게 아파보이지 않는 것이 보통이다. 그래서 그런 전신성 바이러스 감염병을 스마일링 바이러스 감염병이라고 한다.
전신성 박테리아 감염병을 앓을 때는 백혈구 수치가 더 증가되고 C-반응 단백질 혈중 농도가 더 더 증가되며 적혈구 침강 속도가 더 증가되는 것이 보통이다.
|
바이러스 감염병과 박테리아 감염병을 쉽게 감별 진단 할 수 있는 검사가 곧 가능 할 것이라고 한다. 출처; 2011, 7월 15일 Contemporary pediatrics |
Q.
1주 동안 감기를 앓았습니다.
하기 어려운 진료예약을 하고, 먼데서 와서 진료비를 내고 진료를 받았는데 왜 항생제 처방도 안 해 주시는지요.
A.
감기는 바이러스 감염으로 생기는 바이러스 상기도 감염병입니다.
감기 등 바이러스 감염병은 항생제 치료에 효과가 없습니다.
그러나 감기 이외 생명을 위협하는 위중한 전신성 바이러스 감염병, 전신성 박테리아 감염병을 앓고 있는지, 또는 감기 이외 다른 종류의 감염병을 앓고 있는지 감별진단하고 확인하고, 감기를 앓고 있다면 감기 치료법을 의사로부터 배우고 가시니 그 얼마나 좋은 일입니까.
보통 감기는 대개 1~14일 내 다 나을 겁입니다.
Q.
단골 소아청소년과 의사가 10일간 항생제를 처방해 주어 5일 동안 복용했더니 아무 증상 징후가 없어 이제 다 나은 것 같은데 왜 항생제를 처방해 준 대로 5일 동안 더 계속 먹으라고 합니까.
A.
특별한 이유가 없는 한, 의사가 다 복용하라는 기간 동안 처방해준 항생제를 복용해 치료하는 것은 상당히 중요합니다.
의사가 항생제를 일정 기간 동안 복용하라고 처방했는데 환자 마음대로 며칠간 만 먹다가 그만 집어치우는 경우도 있습니다.
감염병을 일으킨 병원체의 종류에 따라, 그 병원체 감염에 의해 생긴 감염병의 종류와 감염병 병소가 있는 신체의 부위에 따라 항생제의 종류를 선택하고 항생제를 투여하는 경로를 선택해 치료합니다.
박테리아 감염병의 종류에 따라 그 감염병을 특히 잘 치료할 수 있는 항생제가 따로 있습니다.그 특정 항생제로 일정한 기간 동안 일정한 투약 경로를 통애 치료해야 한다는 것이 임상경험에 의해서 정해져 있습니다.
환아를 진료하는 대부분의 의사들은 그런 기준에 의해서 감염병의 종류에 따라 적절한 항생제를 선택해서 적절한 기간 동안 항생제로 치료합니다.
그런데 엄마아빠나 환아가 임의대로 의사가 처방한 항생제 치료기간 동안 항생제로 치료를 하지 않으면
그 감염병이 완치되지 앓을 수 있고,
그 감염병을 이르킨 세균에 내성이 생길 수 있고,
국소 감염병을 일으켰던 세균이 전신으로 퍼져 전신 감염병이 생길 수 있고,
국소 감염병이 더 악화될 수도 있고
소위 일부 치료된 감염병이 될 수 있고(Partial treatment)
재발될 수도 있습니다.
즉 원래 있던 감염병이 “일부 치료 감염병(Partially treated infection)”이 될 수 있다.
의사가 처방한 항생제로 치료를 하는 중 어떤 이상이 생기지 않는 한, 의사가 처방한 항생제를 쓰라고 했던 기간 동안 복용해야 합니다.
Q.
어떻게 해서 사람에게 항생제 내성이 생기나요.
A.
사실은 항생제로 치료받는 중 사람에게 내성이 생기는 것이 아니고 박테리아가 항생제에 내성이 생기는 것입니다.
박테리아는 하나의 미생물입니다.
박테리아가 아무리 미세한 생물체이라도 우리인간이 그들을 죽이려고 항생제로 공격하고 그들이 못 살게 모든 조건을 가해도 박테리아는 우리 인간과 공존해 가는 방법을 강구하고 연구합니다.
즉 박테리아를 죽이기 위해 썼던 어떤 항생제에 저항성도 없었고, 그 항생제에 죽었던 박테리아가 그 후 같은 종류의 항생제 치료에 같은 종류의 박테리아가 더 이상 죽지 않는 현상을 내성이라 합니다.
예를 들면, 요즘 황색 포도상구균 균주Strain) 중 어떤 균주는 항생제에 내성이 생겨 황색 포도상구균 감염병을 치료하는 데 문제가 있습니다.
Q.
같은 종류의 병원체 감염으로 생긴 감염병을 같은 종류의 항생제로 치료하는 데 어떤 때는 10일간, 어떤 때는 3주간 치료하라고 하는데 그 이유는 무엇입니까
A.
연구에 의해, 또는 임상 경험적으로, 어떤 감염병을 10일간, 또는 3주간 치료하라고 권장합니다. 그러므로 그때그때마다 의사에게 문의해서 그 이유를 알아보는 것이 중요합니다.
Q.
저의 엄마아빠님께서 저에게 페니실린 알레르기가 있었다고 말씀하셨는데 그것이 사실인지 어떻게 압니까
A.
페니실린에 알레르기가 정말로 있었는지 더 확실하게 알아보려면 페니실린 알레르기 검사를 해야 합니다.
페니실린 알레르기 검사로 페니실린에 알레르기가 정말로 있었는지 알아보기 전에 페니실린에 알레르기가 있다고 진단하고 진료했던 주치의로부터 진료일지를 구해 페니실린 알레르기 가 있다고 진단했는지 확인해 보십시오.
Q.
항생제에 알레르기가 생기는지를 어떻게 압니까.
A.
항생제로 치료를 받을 때는 항생제로 아나필락시스 반응(즉시 알레르기 반응)도 생길 수 있고,
혈청 반응도 생길 수 있고
아르튜스 반응(Arthus reaction) 등도 항생제로 생길 수 있습니다.
어떤 종류의 항생제로 치료받을 때 전신에 두드러기가 나고 피부, 입술, 눈이 붓고 결막 출혈이 생기고 때로는 호흡곤란이 생기면 항생제로 인한 즉시 알레르기 반응(아나필락시스, Anaphylaxis)이 생겼다고 추정 진단을 할 수 있습니다.
아나필락시스가 생기면 생명을 위협할 수 있고 죽을 수 있습니다.
그 항생제로 더 이상 치료받지 말고 즉시 응급 치료를 받아야 합니다.
때로는 불과 몇 분 내에 죽을 수 있습니다.
항생제 알레르기가 있다고 진단을 받았으면 어떤 종류의 항생제에 알레르기가 있었는지 알아보고 어떤 종류의 알레르기가 있었는지 확실히 알아보아야 합니다. 더 자세히 알아보기 위해
단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 문의해야 합니다.
Q.
감염병을 항생제로 치료할 때 치료를 시작 한 후 얼마 후 치료 효과가 나타나나요.
A.
감염병의 종류와 감염병이 있는 신체 부위. 감염병의 증상 징후의 정도에 따라 항생제 치료효과가 나타나는 기간이 다릅니다.
일반적으로 항생제로 48~72시간 정도 치료받은 후 치료 효과가 나타나기 시작하는 것이 보통입니다.
그러나 치료를 시작한 후 증상 징후나 중증도가 더 심해지면
그 항생제로 감염병이 치료되지 않거나
추정으로 진단한 감염명이 맞지 않거나
그 항생제로 부작용이 생기거나,
그 감염병으로 합병증이 생겼는지,
병원체가 내성이 생겼는지 알아보기 위해서 의사에게 바로 연락하는 것이 중요합니다.
Q.
가족 중 누가 감염병을 치료받을 때 쓰다가 남겨 놓은 항생제를 제가 사용해도 되는지요.
A.
아닙니다.
다른 사람에게 처방했던 약은 어떤 종류의 약이든 내 맘대로 나에게 써서는 절대로 안 됩니다.
의사가 처방한 약은 의사의 지시에 따라 일정한 치료 기간 동안, 일정한 약의 용량을 전부 다 써야 하는 것이 치료 원칙입니다.
치료 중 질문이 있으면 의사에게 문의한 후 치료 방법을 바꾸는 것을 결정하십시오.
Antibiotics and 100 Qs& As on antibiotic treatments
Antibiotics (antibacterials)
• When treating bacterial infections
• Antibiotics that can treat bacterial infections by killing the bacteria that cause them, and drugs that cure infections by preventing the bacteria from multiplying in the body and eventually killing the bacteria.
• Collectively called antibiotics, antibacterial agents, or antibiotics.
• Antibiotics are manufactured in several forms.
o Antibiotics in liquid form;
o Antibiotics in powder form;
o Antibiotics in capsule form;
o Antibiotics in egg form (tablets);
o Drops (drop pills),
o Intramuscular injection antibiotics;
o Injectable antibiotics;
o Suppository form that can be placed in the vaginal cavity or anus for treatment
o There are also antibiotics in the form of drops that can be placed on the skin, eyes, into the ear canal or into the nostrils.
o Antibiotics in the form of sprays that can be sprayed into the nasal or oral cavity;
o Antibiotic sprays are available that can be aspirated into the airways.
o There are also antibiotics in the form of ointments or creams that are applied to the skin or mucous membranes.
www.deleepediatrics.com – See Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing – Volume 21 Pediatric Home Nursing – Drugs and Drug Forms. Refer to Classification of antibiotics (antibiotics), types of antibiotics, generic names of antibiotics, trade names of antibiotics, routes of administration of antibiotics, normal doses of antibiotics, and intervals between antibiotics
• There are hundreds of types of antibiotics, and depending on the type of bacteria that caused the infectious disease, the presence or absence of resistance to the bacteria (antibiotic resistance or antibiotic resistance), the type and severity of the infectious disease, the age of the child, the presence or absence of side effects to the antibiotic; It is common to treat infectious diseases by selecting appropriate antibiotics according to the history of allergies, etc.
o Broad-spectrum antibiotics such as cephalosporins, o Estomycin (Erythromycin),
o Antibiotics such as Clarithromycin and Azithromycin are macrolide antibiotics,
o Antibiotics are sometimes classified as bactericidal antibiotics.
• When treating certain infectious diseases, depending on the situation, antibiotic treatment may be empirically started without bacteriological testing before starting treatment.
• However, the most ideal treatment for infectious diseases is to select and treat antibiotics based on the results obtained from Gram stain microscopy, bacterial culture test, and antibiotic susceptibility test.
• However, there are many cases where infectious diseases are treated without bacteriological testing for various reasons.

Picture 1-12. Antibiotic tablets are made in various sizes and shapes. In general, when treating infectious diseases of infants and young children or school-age children, it is inappropriate because they have difficulty taking antibiotics. It is possible to break the pill into a powder and take it, but it is often inappropriate to administer the pill in that way. If you need to break a pill or capsule and take it, ask the doctor or pharmacist who prescribed it. Take according to the directions of Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-11 There are also antibiotics prepared in capsules. These types of antibiotics are not usually prescribed for infants and some school-age children because they are uncomfortable to take. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-13. Infectious diseases can be treated with antibiotic suppositories. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 1-14. Antibiotic ointments can be used to treat skin infections. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-15. Select one or two antibiotics in the form of injections, water drops, pills, plasters, suppositories, etc. depending on the age of the child, the type of antibiotic, the affected area, how mild or serious the infectious disease is, and the home environment. can be treated with Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-16. Even today, there are antibiotics in powder form that can be taken orally to treat infectious diseases. However, it is common to take the powdered antibiotics right before taking the powdered antibiotics without treating the infectious disease.

Photo 1-18. Considering serious life-threatening infectious diseases such as meningitis and sepsis, the age of the child, the type of infectious disease, treatment problems, and the type of antibiotic, it can be treated with intravenous antibiotics or intramuscular injections of antibiotics. Multiple injections of mucositis are treated with multiple injections, especially children, who are afraid of receiving injections and are very reluctant to receive injections because they are painful. Also, adults, like children, hate being treated with multiple injections. These days, a local anesthetic can be applied or sprayed on the area to be injected before the injection. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-17. Antibiotics should be administered in consideration of the child’s age, the location of the infectious disease in the body, the type of infectious disease such as meningitis, sepsis, or impetigo, the type of pathogen that caused the infectious disease, the type of antibiotic, and the problems and circumstances that may arise during treatment. It is a principle to treat infectious diseases by selecting the most appropriate route of administration among intravenous, intramuscular, oral, or other routes of administration. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Questions and Answers on Antibiotic Treatment One hundreds of questions and answers on antibiotic treatments
Q. When I have a systemic infectious disease (systemic infectious disease), how do I distinguish between a systemic bacterial infectious disease (systemic bacterial infectious disease) or a systemic viral infectious disease (viral infectious disease)?
A. In most cases, it is difficult to clearly differentiate clinically, taking into account the symptoms and signs of systemic infectious diseases. In particular, in the early stages of systemic infectious diseases, it is more difficult to make a clinically definitive differential diagnosis without bacteriological testing. In general, when there is a systemic bacterial infection, it is common to have a higher fever or more severe illness.
However, with any systemic viral infection, you may have a high fever, you may be very ill, and your symptoms may be severe.
For this reason, it is often difficult to clearly and easily differentiate whether a person has a systemic bacterial infectious disease or a systemic viral infection, especially in the early stages of the onset.
For this reason, when suffering from systemic infectious diseases, it is important to promptly receive a differential diagnosis of which type of pathogen among these two types of pathogens is being infected.
For reference, in most cases, when a systemic severe bacterial infection occurs, it is normal for the child to be in a toxic state.
When suffering from a systemic viral infection, it is normal for the patient to smile and not look so sick. Therefore, such a systemic viral infection is called a smiling virus infection. In systemic bacterial infections, it is common to have higher white blood cell counts, higher C-reactive protein blood levels, and higher erythrocyte sedimentation rates.
It is said that a test that can easily differentiate between viral and bacterial infections will soon be available. source; July 15, 2011 Contemporary pediatrics
Q.
I had a cold for a week. I made a medical appointment that is difficult to make, and I came from afar and paid for treatment. Why didn’t they even prescribe antibiotics?
A. A cold is a viral upper respiratory tract infection caused by a viral infection. Antibiotics are ineffective for viral infections such as colds. However, how good is it to differentially diagnose and confirm whether you have a serious life-threatening systemic viral infection other than a cold, a systemic bacterial infection, or a type of infectious disease other than a cold, and learn a cold treatment from a doctor if you have a cold? is it work The common cold will usually go away in 1 to 14 days.
Q. A regular pediatrician prescribed antibiotics for 10 days, and after taking them for 5 days, there are no symptoms and everything seems to be fine now.
A. Unless there is a specific reason, it is very important to take the antibiotics prescribed by your doctor for the period your doctor has told you to take. In some cases, the doctor has prescribed antibiotics to be taken for a certain period of time, but the patient stops taking them for a few days at will. The type of antibiotic is selected according to the type of pathogen that caused the infectious disease, the type of infectious disease caused by the pathogen infection and the part of the body where the infectious disease lesion is located, and the route of antibiotic administration is selected for treatment.
Depending on the type of bacterial infectious disease, there is an antibiotic that can treat the infectious disease particularly well. It is determined by clinical experience that the specific antibiotic should be treated through a certain route of administration for a certain period of time.
Most doctors who treat children select the appropriate antibiotic according to the type of infectious disease based on such criteria and treat it with antibiotics for an appropriate period of time.
However, if the mother, father, or child do not take antibiotic treatment during the antibiotic treatment period prescribed by the doctor arbitrarily, The infectious disease may not be cured and may be ill, The bacteria that caused the infectious disease can develop resistance, Bacteria that caused local infectious diseases can spread throughout the body and cause systemic infections. Local infections may get worse It can be a so-called partially treated infectious disease (Partial treatment) It may recur.
That is, the original infectious disease may become a “Partially treated infection”. You should take the antibiotics prescribed by your doctor for as long as your doctor tells you to take them, unless something goes wrong while you are being treated with the antibiotics your doctor prescribes.
Q. How do people develop antibiotic resistance?
A. The fact is that people do not develop resistance while being treated with antibiotics, but bacteria develop resistance to the antibiotic. Bacteria are microbes. Even if bacteria are microscopic organisms, we humans attack them with antibiotics to kill them, and even if we apply all kinds of conditions to kill them, we find and study how bacteria can coexist with us humans.
In other words, resistance to any antibiotic used to kill the bacteria is a phenomenon in which the bacteria killed by the antibiotic no longer die with the same type of antibiotic treatment. For example, some strains of Staphylococcus aureus these days) have become resistant to antibiotics, making it difficult to treat Staphylococcus aureus infections.
Q. Infectious diseases caused by the same pathogen infection are treated with the same type of antibiotic, sometimes for 10 days and sometimes for 3 weeks. Why is that?
A. Research or clinical experience recommends treating certain infectious diseases for 10 days or 3 weeks. Therefore, it is important to check with your doctor from time to time to find out the reason.
Q. My mom and dad told me I had a penicillin allergy, how do I know if it’s true?
A. A penicillin allergy test is needed to determine if you really have an allergy to penicillin. Before you do a penicillin allergy test to find out if you really have a penicillin allergy, check to see if you have been diagnosed with a penicillin allergy by getting a journal from your primary care physician who diagnosed you with a penicillin allergy.
Q. How do you know if you are allergic to antibiotics?
A. When treated with antibiotics, anaphylactic reactions (immediate allergic reactions) may also occur with antibiotics. Serum reactions may also occur. Arthus reaction can also occur with antibiotics. If you are treated with any type of antibiotic, you can make a presumptive diagnosis of an immediate allergic reaction to the antibiotic (anaphylaxis) if you develop body-wide hives, swelling of the skin, lips, and eyes, bleeding from the conjunctiva, and sometimes shortness of breath.
Anaphylaxis can be life-threatening and can result in death. You should no longer be treated with that antibiotic and seek emergency treatment immediately. Sometimes it can die in just a few minutes. If you have been diagnosed with an antibiotic allergy, you need to find out what type of antibiotic you have been allergic to and make sure you know what type of allergy you have. to learn more You should consult your regular pediatrician.
Q. When treating an infectious disease with antibiotics, how long after starting treatment will the therapeutic effect appear?
A. Types of infectious diseases and body parts with infectious diseases. The duration of antibiotic treatment effects varies depending on the severity of the symptoms of the infectious disease. In general, it is normal for the treatment effect to begin to appear after 48 to 72 hours of treatment with antibiotics.
However, if symptoms become more severe or severe after starting treatment, If the antibiotic does not cure the infection, or If the presumptive diagnosis of the infection name does not match, side effects of the antibiotic, or Did the infectious disease cause complications? It is important to contact your doctor right away to see if the pathogen has developed resistance.
Q. Can I use antibiotics left over from someone in my family being treated for an infectious disease?
A. no. You must never use any medicine of any kind on me if I have prescribed it to someone else. The principle of treatment is to use up the entire dose of a given drug over a certain period of treatment according to the doctor’s instructions. If you have any questions during treatment, ask your doctor before deciding to change your treatment.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine